Building a React Chat Interface with a Multilingual Virtual 3D Assistant
Hello everyone, in this blog post, we will guide you through the process of building a chat interface in React with a virtual 3D assistant capable of understanding and responding in different languages, including English, Spanish, German, Italian, Russian and Japanese. This chat interface will enable users to send text messages and record audio messages, with real-time responses displayed. We will be utilizing React components, hooks, and external libraries to create a functional and user-friendly chat experience. Specifically, we will be using Google API services for speech-to-text and text-to-speech capabilities, as well as OpenAI’s ChatGPT for generating the assistant’s responses.
To make our application more visually appealing and responsive, we will use React Next and the “tamagui” library as a template. React Next allows for server-rendered React applications, providing better performance and SEO benefits.
Prerequisites:
Before we dive in, it is important to have a basic understanding of React and its concepts. Familiarity with JavaScript and JSX syntax will also be beneficial. Knowledge of Google API services, OpenAI’s ChatGPT, React Next, and the “tamagui” library is a plus.
Step 1: Set Up the Project
To begin, create a new React project, we can clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/ruslanmv/gpt-anime.git
This is a repo for the gpt-anime project.
Once your project is set up, navigate to the project directory in your terminal
ce gpt-anime
and install the necessary dependencies by running “npm install”.
- Install npm - nvm and node version 18.14.2 are recommended
We are going to use Ubuntu to run this app. If you have windows you can just install
bash
sudo apt apt-get update
sudo apt install npm
sudo apt install curl
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.3/install.sh | bash
source ~/.bashrc
nvm install node
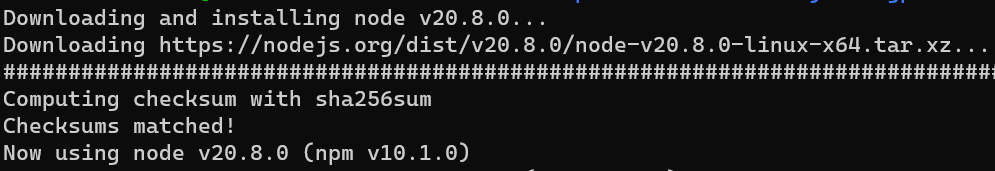
nvm install v18.14.2
- Make sure npm is installed. To check if it’s installed you can run
npm -v
- Install yarn
npm install --global yarn
How to run the project
- Clone the repository
- Add API keys to
.env.localfile
cp .env env.local
Paste your OpenAI API key by adding the OPENAI_API_KEY and add a Google Cloud API key by adding the GOOGLE_API_KEY and repeat it with the NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_API_KEY also environment variables in the .env.local file.
- Install the dependencies - In the root folder of this project Run
yarn install
to install the dependencies
- Run the project - In the root folder of this project ,
Run the following command
yarn web
to start the web server
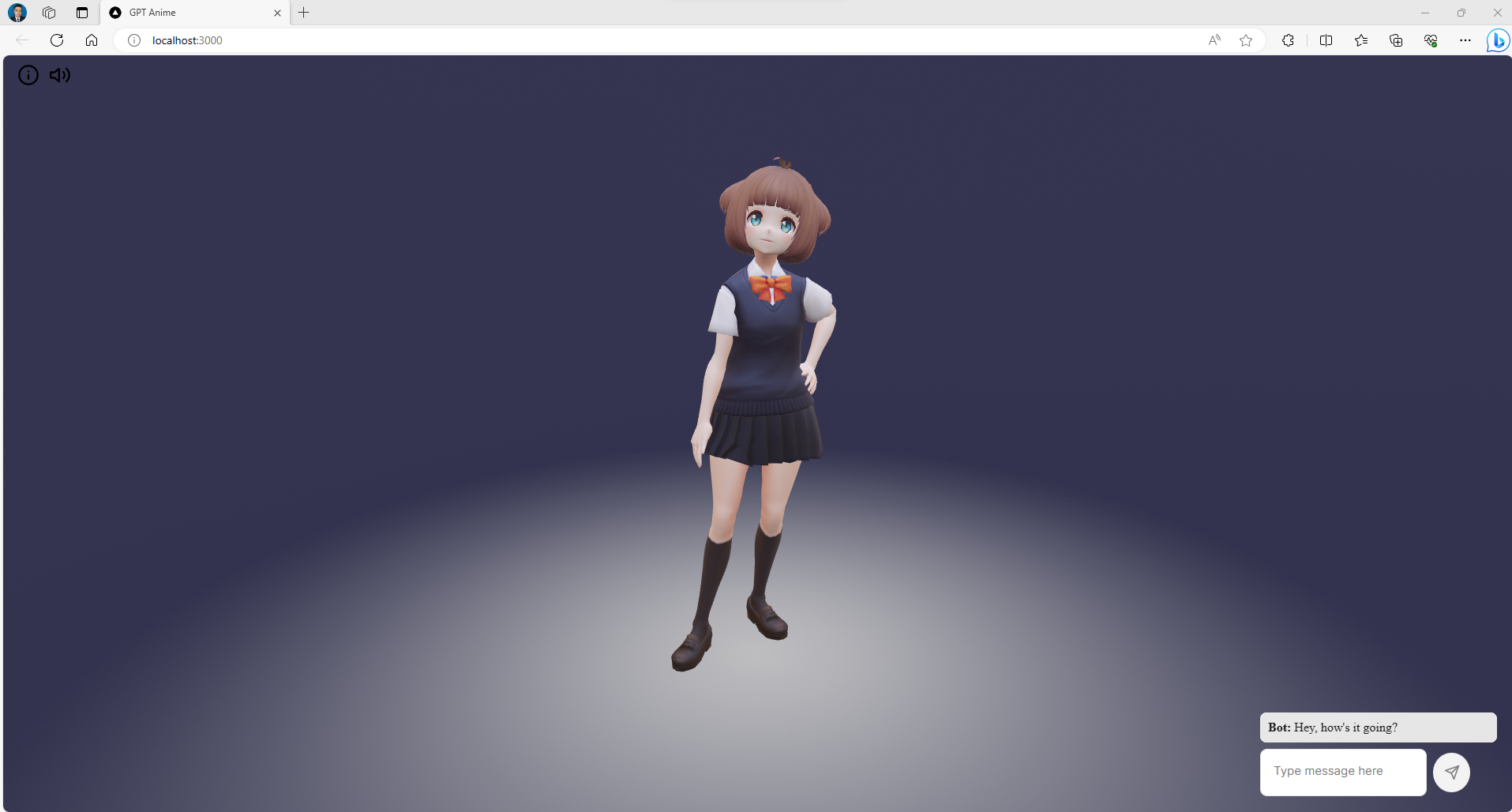
- Navigate to http://localhost:3000 to view the project
- Custom run (optional) If you want to run with optimizer on in dev mode (just for testing, it’s faster to leave it off):
yarn web:extract
To build for production
yarn web:prod
To see debug output to verify the compiler, add // debug as a comment to the top of any file.
Once we have setup our project let us deep dive to the main parts of the program.
Step 2: Main Dependencies of the Chatbot
In your main React component file, the Chat.tsx, we import the required components and hooks from the “tamagui” library. You will also need to import icons from the “@tamagui/lucide-icons” library. Additionally, import the ChatErrors component from “./ChatErrors” and the useChat hook from “./hooks”. Finally, import the recordAndTranscribe function from “./speechToText”.
In addition to the existing imports, you should also import the required dependencies for Google API services and OpenAI’s ChatGPT
import { Mic, Send, StopCircle } from "@tamagui/lucide-icons";
import { memo, useState } from "react";
import {
Button,
ScrollView,
Spinner,
StackPropsBase,
Text,
TextArea,
XStack,
YStack,
useMedia,
} from "tamagui";
import { ChatErrors } from "./ChatErrors";
import { ChatHookReturnType, useChat } from "./hooks";
import { recordAndTranscribe } from "./speechToText";
Step 3: Define Constants and Types
In the same file, define any necessary constants such as OPENAI_TIMEOUT_MILLISECONDS, CHAT_MESSAGES_URL, alpha, and MAX_CHARS. Also, define types for ChatMessage and ChatServerResponse to ensure type safety within your program.
const OPENAI_TIMEOUT_MILLISECONDS = 5_000;
const CHAT_MESSAGES_URL = "/api/chat";
const alpha = "0.9";
export const MAX_CHARS = 300;
export type ChatMessage = {
role: "user" | "system" | "assistant";
content: string;
};
export type ChatServerResponse =
| string
| {
error: string;
};
Step 4: Implement Functions
Next, implement the necessary functions for sending messages and recording audio. The send function handles user-initiated message sending, appending messages to the chat, and sending them to the backend.
const send = async (
textAreaRef: ChatHookReturnType["textAreaRef"],
setChatState: ChatHookReturnType["setChatState"],
appendBotMessage: ChatHookReturnType["appendBotMessage"],
appendUserMessage: ChatHookReturnType["appendUserMessage"],
audioReceivedCallback: ChatProps["audioReceivedCallback"],
isLoadingMessage: boolean
) => {
// Function implementation...
};
The RecordingButton function manages the recording and transcription of audio messages.
const RecordingButton = async (
textAreaRef: ChatHookReturnType["textAreaRef"], // Reference to the text input field
setChatState: ChatHookReturnType["setChatState"], // Function to update the chat state
appendBotMessage: ChatHookReturnType["appendBotMessage"], // Function to add a bot message to the chat
appendUserMessage: ChatHookReturnType["appendUserMessage"], // Function to add a user message to the chat
audioReceivedCallback: ChatProps["audioReceivedCallback"], // Callback for receiving audio responses
isLoadingMessage: boolean, // Flag to indicate if a message is currently being sent,
setMicIcon: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<React.ReactNode>>, // Add this parameter
setIsRecording: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<React.ReactNode>>, // Add this parameter
currentLanguage: string // Add this parameter
) => {
if (isLoadingMessage) {
// If a message is already being sent, do nothing
return;
}
// We got the current language from the state setLanguage
console.log(' language to recognize :', currentLanguage);
// Call the recordAndTranscribe function to get the transcribed text from the backend
const textInput = await recordAndTranscribe(currentLanguage);
setMicIcon(<Mic size="$1" />);
setIsRecording(false);
if (textAreaRef?.current && textInput) {
if (textInput.length > MAX_CHARS) {
// If the message is too long, show an error message
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
errorMessage: `Please give a message with ${MAX_CHARS} characters or less.`,
}));
return;
}
textAreaRef.current.clear();
textAreaRef.current.focus();
// Get the last two messages to send to the backend
const allMessages = appendUserMessage(textInput);
const messagesToSendToBackend = allMessages.slice(-2);
try {
// Send the messages to the backend, Sends a POST request to the backend.
await sendMessages(messagesToSendToBackend, setChatState, appendBotMessage, audioReceivedCallback);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error sending message from mic:", error);
}
}
};
The sendMessages function is responsible for sending messages to the backend and handling the server response. Make sure to handle any errors that may occur during these processes.
// Function to send messages to the backend
const sendMessages = async (messagesToSendToBackend, setChatState, appendBotMessage, audioReceivedCallback) => {
// Set the loading state to indicate that a message is being sent
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
isLoadingMessage: true,
}));
try {
const response = await fetch(CHAT_MESSAGES_URL, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(messagesToSendToBackend.map((message) => ({ content: message.content, role: message.role })),
)
});
// We have a response! Maybe it's an error, but not worries. We'll handle it below.
//clearTimeout(timeoutId);
if (!response.ok) {
// If the response is not okay, handle the error
const result = await response.json();
throw new Error(result.error);
}
const jsonResponse = await response.json();
// Response has 3 parts: text , audio and language
// 1. Append the text response from the backend to the chat's scroll view.
appendBotMessage({ content: jsonResponse.text, role: "assistant" });
// 2. Play the audio response (if available)
const audioContent = await jsonResponse.audio;
const audio = new Audio(`data:audio/mpeg;base64,${audioContent}`);
audioReceivedCallback(audio);
// 3. We got the language and update the current state to this language
const newLanguage = await jsonResponse.language;
console.log(' language retrieved :', newLanguage);
// Adding the new language to the chat state
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
language: newLanguage,
}));
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error in sendMessages:", error);
// Update the chat state with an error message
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
errorMessage: error.message || "Error: something went wrong.",
}));
} finally {
// Ensure the chat scrolls to the latest message
//messagesContainerRef.current?.scrollToEnd({ animated: true });
// Reset the loading state
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
isLoadingMessage: false,
}));
}
};
Step 5: Create the PrintMessages Component
To display the chat messages, create a PrintMessages component. This component maps over the messages and renders each message as a Text component. You can customize the appearance of the messages based on the role (user, system, or assistant) using conditional styling.
// This component takes care of showing the messages in the chat's scroll view.
const PrintMessages = memo(({ messages }: { messages: ChatMessage[] }) => {
return (
<>
{messages.map((message, index) => {
const isBot = message.role === "assistant";
const contentLines = message.content.split(/\n+/);
return contentLines.map((line, lineIndex) => (
<Text
backgroundColor={isBot ? `rgba(230, 230, 230,${alpha})` : undefined}
py={8}
px={10}
key={`${index}-${lineIndex}`}
lineHeight="1.4"
>
<Text
fontWeight="600"
// color={isBot ? "$blue4Dark" : undefined}
>
{" "}
{lineIndex === 0 && (isBot ? "Bot:" : "You:")}
</Text>{" "}
{line}
</Text>
));
})}
</>
);
});
Step 6: Build the Chat Interface
In your main component, utilize the useChat hook to manage the chat state. This hook provides functions to append messages, set the chat state, and manage the text input field’s reference. Use the provided callbacks to handle audio responses.
Render the chat interface using the YStack and XStack components from the “tamagui” library. Implement a ScrollView component to display the chat messages. Include a TextArea component for user input and buttons for sending text messages and recording audio messages. Use conditional rendering to display a loading spinner while messages are being sent.
// Main chat component.
export const Chat = ({ audioReceivedCallback, ...stackProps }: ChatProps) => {
const {
chatState,
setChatState,
textAreaRef,
messagesContainerRef,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
} = useChat();
const media = useMedia();
const { isLoadingMessage } = chatState;
const [isRecording, setIsRecording] = useState(false);
const [micIcon, setMicIcon] = useState(<Mic size="$1" />);
// Constant numbers:
const regularMessagesBoxHeight = 300;
const smallMessagesBoxHeight = 170;
const width = 300;
const textAreaHeight = 60;
const buttonMarginLeft = 8;
const buttonSize = 50;
const isSmall = media.xs;
const handleButtonPress = async () => {
//const { chatState } = useChat();
const language = chatState.language;
if (isRecording) {
// Stop recording
setIsRecording(false);
// Change the icon back to Mic
setMicIcon(<Mic size="$1" />);
await RecordingButton(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage,
setMicIcon,
setIsRecording,
language
);
} else {
// Start recording
setIsRecording(true);
// Change the icon to StopCircle
setMicIcon(<StopCircle size="$1" />);
await RecordingButton(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage,
setMicIcon,
setIsRecording,
language
);
}
};
return (
<YStack
ai="center"
jc="flex-end"
position="absolute"
bottom="0"
right="0"
m={20}
w={width}
maxWidth="90vw"
{...stackProps}
>
<ScrollView
ref={messagesContainerRef}
maxHeight={isSmall ? smallMessagesBoxHeight : regularMessagesBoxHeight}
backgroundColor={scrollViewBackgroundColor}
mb={8}
br={8}
width="100%"
onContentSizeChange={() => messagesContainerRef.current?.scrollToEnd({ animated: true })}
>
<PrintMessages messages={chatState.messages} />
</ScrollView>
<XStack ai="center" width="100%">
{/* DOCS: https://necolas.github.io/react-native-web/docs/text-input/ */}
<TextArea
// TODO: Get the real TextInput type from react native, and remove the below @ts-expect-error
// @ts-expect-error
ref={textAreaRef}
h={textAreaHeight}
// w={width - buttonSize - buttonMarginLeft}
placeholder={chatState.isLoadingMessage ? "Loading message..." : "Type message here"}
disabled={chatState.isLoadingMessage}
returnKeyType="send"
multiline
blurOnSubmit={false}
onKeyPress={(e) => {
// Handle browser submit.
if (e.nativeEvent.key === "Enter" && "shiftKey" in e && !e.shiftKey) {
e.preventDefault(); // Prevent a new line from being added
send(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage
);
}
}}
onSubmitEditing={() =>
// Handle Android and iOS submit.
send(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage
)
}
maxLength={MAX_CHARS}
onChangeText={(text: string) => setChatState({ ...chatState, charCount: text.length })}
/>
{isLoadingMessage ? (
<Spinner
height={buttonSize}
width={buttonSize}
size="small"
jc="center"
ai="center"
color="$gray10"
ml={buttonMarginLeft}
backgroundColor="#F3F3F3"
br="100%"
/>
) : (
<>
<Button
size={buttonSize}
ml={buttonMarginLeft}
icon={<Send size="$1" />}
br="100%"
onPress={() =>
send(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage
)
}
/>
<Button
size={buttonSize}
ml={buttonMarginLeft}
//icon={<Mic size="$1" />}
//icon={isRecording ? <StopCircle size="$1" /> : <Mic size="$1" />}
icon={micIcon}
br="100%"
onPress={handleButtonPress}
/>
</>
)}
</XStack>
<ChatErrors errorMessage={chatState.errorMessage} charCount={chatState.charCount} />
</YStack>
);
};
Step 7: Test and Refine
Once your chat interface is implemented, thoroughly test it to ensure it functions as expected. Test sending text messages, recording audio messages, and receiving responses from the backend. Refine the interface as needed, adjusting the styling and functionality to suit your specific requirements.
Full code program code here Chat.tsx
import { Mic, Send, StopCircle } from "@tamagui/lucide-icons";
import { memo, useState } from "react";
import {
Button,
ScrollView,
Spinner,
StackPropsBase,
Text,
TextArea,
XStack,
YStack,
useMedia,
} from "tamagui";
import { ChatErrors } from "./ChatErrors";
import { ChatHookReturnType, useChat } from "./hooks";
import { recordAndTranscribe } from "./speechToText";
//import { recordAndTranscribe } from "next-app/speechToText"; // Replace with your actual apps/next package name
const OPENAI_TIMEOUT_MILLISECONDS = 5_000;
const CHAT_MESSAGES_URL = "/api/chat";
const alpha = "0.9";
const scrollViewBackgroundColor = `rgba(255, 255, 255,${alpha})`;
export const MAX_CHARS = 300;
export type ChatMessage = {
role: "user" | "system" | "assistant";
content: string;
};
export type ChatServerResponse =
| string
| {
error: string;
};
type ChatProps = StackPropsBase & {
audioReceivedCallback: (audio: HTMLAudioElement | null) => void;
};
// This function is called when a user wants to send a message to the backend. It does the following:
// 1. Appends the user's message to the existing messages array. This shows the message in the chat's scroll view.
// 2. Sends a POST request to the backend and waits for the server side events.
// Function to send a message to the backend and handle responses
const send = async (
textAreaRef: ChatHookReturnType["textAreaRef"], // Reference to the text input field
setChatState: ChatHookReturnType["setChatState"], // Function to update the chat state
appendBotMessage: ChatHookReturnType["appendBotMessage"], // Function to add a bot message to the chat
appendUserMessage: ChatHookReturnType["appendUserMessage"], // Function to add a user message to the chat
audioReceivedCallback: ChatProps["audioReceivedCallback"], // Callback for receiving audio responses
isLoadingMessage: boolean // Flag to indicate if a message is currently being sent
) => {
if (isLoadingMessage) {
// If a message is already being sent, do nothing
return;
}
const textInput = textAreaRef?.current?.value;
if (textAreaRef?.current && textInput) {
if (textInput.length > MAX_CHARS) {
// If the message is too long, show an error message
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
errorMessage: `Please enter a message with ${MAX_CHARS} characters or less.`,
}));
return;
}
textAreaRef.current.clear();
textAreaRef.current.focus();
// Get the last two messages to send to the backend
const allMessages = appendUserMessage(textInput);
const messagesToSendToBackend = allMessages.slice(-2);
try {
// Send the messages to the backend, Sends a POST request to the backend.
await sendMessages(messagesToSendToBackend, setChatState, appendBotMessage, audioReceivedCallback);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error sending messages:", error);
}
}
};
//const [Language, setLanguage] = useState("english");
const RecordingButton = async (
textAreaRef: ChatHookReturnType["textAreaRef"], // Reference to the text input field
setChatState: ChatHookReturnType["setChatState"], // Function to update the chat state
appendBotMessage: ChatHookReturnType["appendBotMessage"], // Function to add a bot message to the chat
appendUserMessage: ChatHookReturnType["appendUserMessage"], // Function to add a user message to the chat
audioReceivedCallback: ChatProps["audioReceivedCallback"], // Callback for receiving audio responses
isLoadingMessage: boolean, // Flag to indicate if a message is currently being sent,
setMicIcon: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<React.ReactNode>>, // Add this parameter
setIsRecording: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<React.ReactNode>>, // Add this parameter
currentLanguage: string // Add this parameter
) => {
if (isLoadingMessage) {
// If a message is already being sent, do nothing
return;
}
// We got the current language from the state setLanguage
console.log(' language to recognize :', currentLanguage);
// Call the recordAndTranscribe function to get the transcribed text from the backend
const textInput = await recordAndTranscribe(currentLanguage);
setMicIcon(<Mic size="$1" />);
setIsRecording(false);
if (textAreaRef?.current && textInput) {
if (textInput.length > MAX_CHARS) {
// If the message is too long, show an error message
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
errorMessage: `Please give a message with ${MAX_CHARS} characters or less.`,
}));
return;
}
textAreaRef.current.clear();
textAreaRef.current.focus();
// Get the last two messages to send to the backend
const allMessages = appendUserMessage(textInput);
const messagesToSendToBackend = allMessages.slice(-2);
try {
// Send the messages to the backend, Sends a POST request to the backend.
await sendMessages(messagesToSendToBackend, setChatState, appendBotMessage, audioReceivedCallback);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error sending message from mic:", error);
}
}
};
// Function to send messages to the backend
const sendMessages = async (messagesToSendToBackend, setChatState, appendBotMessage, audioReceivedCallback) => {
// Set the loading state to indicate that a message is being sent
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
isLoadingMessage: true,
}));
try {
const response = await fetch(CHAT_MESSAGES_URL, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(messagesToSendToBackend.map((message) => ({ content: message.content, role: message.role })),
)
});
// We have a response! Maybe it's an error, but not worries. We'll handle it below.
//clearTimeout(timeoutId);
if (!response.ok) {
// If the response is not okay, handle the error
const result = await response.json();
throw new Error(result.error);
}
const jsonResponse = await response.json();
// Response has 3 parts: text , audio and language
// 1. Append the text response from the backend to the chat's scroll view.
appendBotMessage({ content: jsonResponse.text, role: "assistant" });
// 2. Play the audio response (if available)
const audioContent = await jsonResponse.audio;
const audio = new Audio(`data:audio/mpeg;base64,${audioContent}`);
audioReceivedCallback(audio);
// 3. We got the language and update the current state to this language
const newLanguage = await jsonResponse.language;
console.log(' language retrieved :', newLanguage);
// Adding the new language to the chat state
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
language: newLanguage,
}));
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error in sendMessages:", error);
// Update the chat state with an error message
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
errorMessage: error.message || "Error: something went wrong.",
}));
} finally {
// Ensure the chat scrolls to the latest message
//messagesContainerRef.current?.scrollToEnd({ animated: true });
// Reset the loading state
setChatState((currentState) => ({
...currentState,
isLoadingMessage: false,
}));
}
};
// This component takes care of showing the messages in the chat's scroll view.
const PrintMessages = memo(({ messages }: { messages: ChatMessage[] }) => {
return (
<>
{messages.map((message, index) => {
const isBot = message.role === "assistant";
const contentLines = message.content.split(/\n+/);
return contentLines.map((line, lineIndex) => (
<Text
backgroundColor={isBot ? `rgba(230, 230, 230,${alpha})` : undefined}
py={8}
px={10}
key={`${index}-${lineIndex}`}
lineHeight="1.4"
>
<Text
fontWeight="600"
// color={isBot ? "$blue4Dark" : undefined}
>
{" "}
{lineIndex === 0 && (isBot ? "Bot:" : "You:")}
</Text>{" "}
{line}
</Text>
));
})}
</>
);
});
// Main chat component.
export const Chat = ({ audioReceivedCallback, ...stackProps }: ChatProps) => {
const {
chatState,
setChatState,
textAreaRef,
messagesContainerRef,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
} = useChat();
const media = useMedia();
const { isLoadingMessage } = chatState;
const [isRecording, setIsRecording] = useState(false);
const [micIcon, setMicIcon] = useState(<Mic size="$1" />);
// Constant numbers:
const regularMessagesBoxHeight = 300;
const smallMessagesBoxHeight = 170;
const width = 300;
const textAreaHeight = 60;
const buttonMarginLeft = 8;
const buttonSize = 50;
const isSmall = media.xs;
const handleButtonPress = async () => {
//const { chatState } = useChat();
const language = chatState.language;
if (isRecording) {
// Stop recording
setIsRecording(false);
// Change the icon back to Mic
setMicIcon(<Mic size="$1" />);
await RecordingButton(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage,
setMicIcon,
setIsRecording,
language
);
} else {
// Start recording
setIsRecording(true);
// Change the icon to StopCircle
setMicIcon(<StopCircle size="$1" />);
await RecordingButton(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage,
setMicIcon,
setIsRecording,
language
);
}
};
return (
<YStack
ai="center"
jc="flex-end"
position="absolute"
bottom="0"
right="0"
m={20}
w={width}
maxWidth="90vw"
{...stackProps}
>
<ScrollView
ref={messagesContainerRef}
maxHeight={isSmall ? smallMessagesBoxHeight : regularMessagesBoxHeight}
backgroundColor={scrollViewBackgroundColor}
mb={8}
br={8}
width="100%"
onContentSizeChange={() => messagesContainerRef.current?.scrollToEnd({ animated: true })}
>
<PrintMessages messages={chatState.messages} />
</ScrollView>
<XStack ai="center" width="100%">
{/* DOCS: https://necolas.github.io/react-native-web/docs/text-input/ */}
<TextArea
// TODO: Get the real TextInput type from react native, and remove the below @ts-expect-error
// @ts-expect-error
ref={textAreaRef}
h={textAreaHeight}
// w={width - buttonSize - buttonMarginLeft}
placeholder={chatState.isLoadingMessage ? "Loading message..." : "Type message here"}
disabled={chatState.isLoadingMessage}
returnKeyType="send"
multiline
blurOnSubmit={false}
onKeyPress={(e) => {
// Handle browser submit.
if (e.nativeEvent.key === "Enter" && "shiftKey" in e && !e.shiftKey) {
e.preventDefault(); // Prevent a new line from being added
send(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage
);
}
}}
onSubmitEditing={() =>
// Handle Android and iOS submit.
send(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage
)
}
maxLength={MAX_CHARS}
onChangeText={(text: string) => setChatState({ ...chatState, charCount: text.length })}
/>
{isLoadingMessage ? (
<Spinner
height={buttonSize}
width={buttonSize}
size="small"
jc="center"
ai="center"
color="$gray10"
ml={buttonMarginLeft}
backgroundColor="#F3F3F3"
br="100%"
/>
) : (
<>
<Button
size={buttonSize}
ml={buttonMarginLeft}
icon={<Send size="$1" />}
br="100%"
onPress={() =>
send(
textAreaRef,
setChatState,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
audioReceivedCallback,
isLoadingMessage
)
}
/>
<Button
size={buttonSize}
ml={buttonMarginLeft}
//icon={<Mic size="$1" />}
//icon={isRecording ? <StopCircle size="$1" /> : <Mic size="$1" />}
icon={micIcon}
br="100%"
onPress={handleButtonPress}
/>
</>
)}
</XStack>
<ChatErrors errorMessage={chatState.errorMessage} charCount={chatState.charCount} />
</YStack>
);
};
Summary of the previous program: … Structure of the program
- Import necessary libraries and components:
- The program imports various components and hooks from the “tamagui” library, such as Button, ScrollView, Spinner, Text, TextArea, XStack, YStack, and useMedia.
- It also imports icons from the “@tamagui/lucide-icons” library.
- Additionally, it imports the ChatErrors component from “./ChatErrors” and the useChat hook from “./hooks”.
- Finally, it imports the recordAndTranscribe function from “./speechToText”.
- Define constants and types:
- The program defines constants such as OPENAI_TIMEOUT_MILLISECONDS, CHAT_MESSAGES_URL, alpha, and MAX_CHARS.
- It also defines types for ChatMessage and ChatServerResponse.
- Define functions:
- The send function is responsible for handling user-initiated message sending, appending messages to the chat, and sending them to the backend.
- The RecordingButton function manages the recording and transcription of audio messages.
- The sendMessages function is responsible for sending messages to the backend and handling the server response.
- The PrintMessages component is responsible for displaying the chat messages in a scroll view.
- The Chat component is the main chat interface, utilizing the useChat hook to manage the chat state and providing callbacks for audio responses.
- Render the Chat component:
- The program renders the Chat component, passing in the audioReceivedCallback prop.
Backend Utils: backendUtils.ts
import { ChatMessage } from "@my/ui/types/Chat";
import { createParser, ParsedEvent, ReconnectInterval } from "eventsource-parser";
export type OpenAIStreamPayload = {
model: string;
messages: ChatMessage[];
temperature: number;
top_p: number;
frequency_penalty: number;
presence_penalty: number;
max_tokens: number;
stream: boolean;
n: number;
};
export async function OpenAIStream(payload: OpenAIStreamPayload) {
const encoder = new TextEncoder();
const decoder = new TextDecoder();
let counter = 0;
const res = await fetch("https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions", {
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY ?? ""}`,
},
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(payload),
});
const stream = new ReadableStream({
async start(controller) {
// callback
function onParse(event: ParsedEvent | ReconnectInterval) {
if (event.type === "event") {
const data = event.data;
// https://beta.openai.com/docs/api-reference/completions/create#completions/create-stream
if (data === "[DONE]") {
controller.close();
return;
}
try {
const json = JSON.parse(data);
const text = json.choices[0].delta?.content || "";
if (counter < 2 && (text.match(/\n/) || []).length) {
// this is a prefix character (i.e., "\n\n"), do nothing
return;
}
const queue = encoder.encode(text);
controller.enqueue(queue);
counter++;
} catch (e) {
// maybe parse error
controller.error(e);
}
}
}
// stream response (SSE) from OpenAI may be fragmented into multiple chunks
// this ensures we properly read chunks and invoke an event for each SSE event stream
const parser = createParser(onParse);
// https://web.dev/streams/#asynchronous-iteration
for await (const chunk of res.body as any) {
parser.feed(decoder.decode(chunk));
}
},
});
return stream;
}
export type OpenAIPayload = {
model: string;
messages: Array<{ role: string; content: string }>;
temperature: number;
top_p: number;
frequency_penalty: number;
presence_penalty: number;
max_tokens: number;
n: number;
};
export type OpenAIResponse = {
id: string;
object: string;
created: number;
model: string;
usage: {
prompt_tokens: number;
completion_tokens: number;
total_tokens: number;
};
choices: Array<{
message: {
role: string;
content: string;
};
finish_reason: string;
index: number;
}>;
};
export const OpenAI = async (payload: OpenAIPayload): Promise<OpenAIResponse> => {
const response = await fetch("https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY}`,
},
body: JSON.stringify(payload),
});
if (!response.ok) {
const errorData = await response.json();
throw new Error(`OpenAI API Error: ${errorData.error.message}`);
}
return await response.json();
};
// Modified synthesizeSpeechMulti function
export async function synthesizeSpeechMulti(text: string): Promise<{ audioContent: string, language: string }> {
if (!process.env.GOOGLE_API_KEY) {
throw new Error("GOOGLE_API_KEY not found in the environment");
}
if (typeof text !== "string") {
throw new Error(`Invalid input type: ${typeof text}. Type has to be text or SSML.`);
}
const language = await detectLanguage(text);
let languageCode;
let voiceName;
let ssmlGender;
//https://cloud.google.com/text-to-speech/docs/voices
switch (language) {
case "english":
languageCode = "en-US";
voiceName = "en-US-Neural2-H";
ssmlGender = "FEMALE";
break;
case "spanish":
languageCode = "es-US";
voiceName = "es-US-Neural2-A";
ssmlGender = "FEMALE";
break;
case "italian":
languageCode = "it-IT";
voiceName = "it-IT-Neural2-A";
ssmlGender = "FEMALE";
break;
case "russian":
languageCode = "ru-RU";
voiceName = "ru-RU-Standard-C";
ssmlGender = "FEMALE";
break;
case "german":
languageCode = "de-DE";
voiceName = "de-DE-Neural2-F";
ssmlGender = "FEMALE";
break;
case "japanese":
languageCode = "ja-JP";
voiceName = "ja-JP-Neural2-B";
ssmlGender = "FEMALE";
break;
default:
throw new Error(`Unsupported language: ${language}`);
}
const apiKey = process.env.GOOGLE_API_KEY;
const apiURL = `https://texttospeech.googleapis.com/v1/text:synthesize?key=${apiKey}`;
const requestBody = {
input: {
text,
},
voice: {
languageCode,
name: voiceName,
ssmlGender,
},
audioConfig: {
audioEncoding: "MP3",
},
};
const response = await fetch(apiURL, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(requestBody),
});
if (!response.ok) {
const errorData = await response.json();
throw new Error(`Google Cloud TTS API Error: ${errorData.error.message}`);
}
const responseData = await response.json();
const audioContent = responseData.audioContent;
return { audioContent, language };
}
… Here, we will create a TypeScript module called backendUtils.ts that contains several functions related to interacting with external APIs and performing various tasks. The functions include OpenAIStream, OpenAI, recursiveStreamEnqueue, streamMock, synthesizeSpeech, detectLanguage, and synthesizeSpeechMulti. Each function serves a specific purpose, such as making API requests and handling audio data.
Speech to Text: speechToText.tsx
export class AudioRecorder {
private recorder: MediaRecorder;
private audioChunks: Blob[];
constructor(stream: MediaStream) {
this.recorder = new MediaRecorder(stream);
this.audioChunks = [];
this.recorder.addEventListener('dataavailable', this.handleDataAvailable);
}
private handleDataAvailable = (event: BlobEvent) => {
if (event.data.size > 0) {
this.audioChunks.push(event.data);
}
};
start() {
this.recorder.start();
}
stop(): Promise<Blob> {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
this.recorder.addEventListener('stop', () => {
resolve(new Blob(this.audioChunks));
});
this.recorder.stop();
});
}
}
export async function recordAndTranscribe(language: string): Promise<string> {
const stream = await navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({ audio: true });
const audioRecorder = new AudioRecorder(stream);
audioRecorder.start();
return new Promise<string>(async (resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(async () => {
try {
const audioBlob = await audioRecorder.stop();
console.log('audioBlob:', audioBlob); // Print audioBlob in the log
// Play the recorded sound
const audioURL = URL.createObjectURL(audioBlob);
const audio = new Audio(audioURL);
//audio.play();
const transcription = await speechToTextMulti(audioBlob, language);
if (typeof transcription === 'string') {
resolve(transcription);
} else {
reject(new Error('Invalid transcription'));
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}, 5000);
});
}
// Function to convert audio blob to base64 encoded string
const audioBlobToBase64 = (blob) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onloadend = () => {
const arrayBuffer = reader.result;
let base64Audio;
if (typeof arrayBuffer === 'string') {
base64Audio = btoa(arrayBuffer);
} else if (arrayBuffer instanceof ArrayBuffer) {
const uint8Array = new Uint8Array(arrayBuffer);
base64Audio = btoa(
uint8Array.reduce(
(data, byte) => data + String.fromCharCode(byte),
''
)
);
} else {
reject('Invalid array buffer');
return;
}
resolve(base64Audio);
};
reader.onerror = reject;
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(blob);
});
};
async function speechToTextMulti(audioBlob, language) {
return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
if (!process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_API_KEY) {
throw new Error("GOOGLE_API_KEY not found in the process.env environment");
}
const apiKey = process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_API_KEY;
console.log('Current State Language for Speech to Text :', language);
const languageCodeMapping = {
english: "en-US",
spanish: "es-ES",
italian: "it-IT",
russian: "ru-RU",
german: "de-DE",
japanese: "ja-JP",
};
const languageCode = languageCodeMapping[language] || "en-US";
try {
const base64Audio = await audioBlobToBase64(audioBlob);
const startTime = performance.now();
const requestOptions = {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
config: {
encoding: 'WEBM_OPUS',
sampleRateHertz: 48000,
languageCode: languageCode,
},
audio: {
content: base64Audio,
},
}),
};
const response = await fetch(
`https://speech.googleapis.com/v1/speech:recognize?key=${apiKey}`,
requestOptions
);
const data = await response.json();
const endTime = performance.now();
const elapsedTime = endTime - startTime;
console.log('Voice Recognition - Time taken (ms):', elapsedTime);
if (data.results && data.results.length > 0) {
const transcription = data.results[0].alternatives[0].transcript;
resolve(transcription);
} else {
reject('No transcription available');
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
});
}
The code provided in speechToText.tsx defines a class called AudioRecorder and two async functions called recordAndTranscribe and speechToTextMulti. These functions allow for recording audio and transcribing it using the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API.
React Hooks :hooks.ts
And finally we need a custom React Hook hooks.ts for managing chat functionality in a chat application. It is written in TypeScript to be designed for a React Native application. The main parts of the code and their functions are:
- Imports: Importing useRef and useState hooks from “react” and ChatMessage type from “./Chat”.
import { useRef, useState } from "react";
import { ChatMessage } from "./Chat";
- Type declarations: Defining custom types MessagesContainerRef and ReactNativeTextInput.
type MessagesContainerRef = HTMLElement & {
scrollToEnd(options?: { animated?: boolean }): void;
};
type ReactNativeTextInput = {
clear: () => void;
focus: () => void;
value: string;
} | null;
- dummyMessages: An array of dummy chat messages for initial state.
let dummyMessages: ChatMessage[] = [];
dummyMessages = [{ role: "assistant", content: "Hey, how's it going?" }];
- ChatHookState type: Represents the state of the chat, including messages, loading state, error messages, character count, and language.
export type ChatHookState = {
messages: ChatMessage[];
isLoadingMessage: boolean;
errorMessage: string;
charCount: number;
language: string;
};
- ChatHookReturnType type: Represents the return type of the custom hook, including chat state, setters, ref objects, and functions for appending messages from both the bot and the user.
export type ChatHookReturnType = {
chatState: ChatHookState;
setChatState: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<ChatHookState>>;
textAreaRef: React.RefObject<ReactNativeTextInput>;
messagesContainerRef: React.RefObject<MessagesContainerRef>;
appendBotMessage: (botMessage: ChatMessage) => void;
appendUserMessage: (userMessage: string) => ChatMessage[];
};
-
useChat function: The custom hook itself, which initializes the state, ref objects, and functions for managing the chat.
- textAreaRef: A ref object for the text input element.
- messagesContainerRef: A ref object for the messages container element.
- chatState and setChatState: State and setter for managing chat-related data, such as messages, error messages, and language.
- appendBotMessage function: Appends a bot message to the chatState, updating the existing message if necessary.
- appendUserMessage function: Appends a user message to the chatState and updates the chat’s scroll view.
export const useChat = (): ChatHookReturnType => {
const textAreaRef = useRef<ReactNativeTextInput>(null);
const messagesContainerRef = useRef<MessagesContainerRef>(null);
const [chatState, setChatState] = useState<ChatHookState>({
charCount: 0,
errorMessage: "",
messages: dummyMessages,
isLoadingMessage: false,
language: "english",
});
const appendBotMessage = (botMessage: ChatMessage) => {
/* ... */
};
const appendUserMessage = (userMessage: string): ChatMessage[] => {
/* ... */
};
return {
chatState,
setChatState,
textAreaRef,
messagesContainerRef,
appendBotMessage,
appendUserMessage,
};
};
The useChat hook can be used in a React component to manage the chat functionality, handle user input, and update the chat UI based on the current state
Conclusion: In this tutorial, we have walked through the process of building a chat interface in React. By utilizing React components, hooks, and external libraries, we were able to create a functional and user-friendly chat experience. We covered the steps involved in setting up the project, importing dependencies, defining constants and types, implementing functions, and creating the chat interface. Additionally, we discussed testing and refining the chat interface to ensure its proper functionality. Feel free to customize and expand upon this chat interface to suit your specific project requirements.
You can play with different languages:
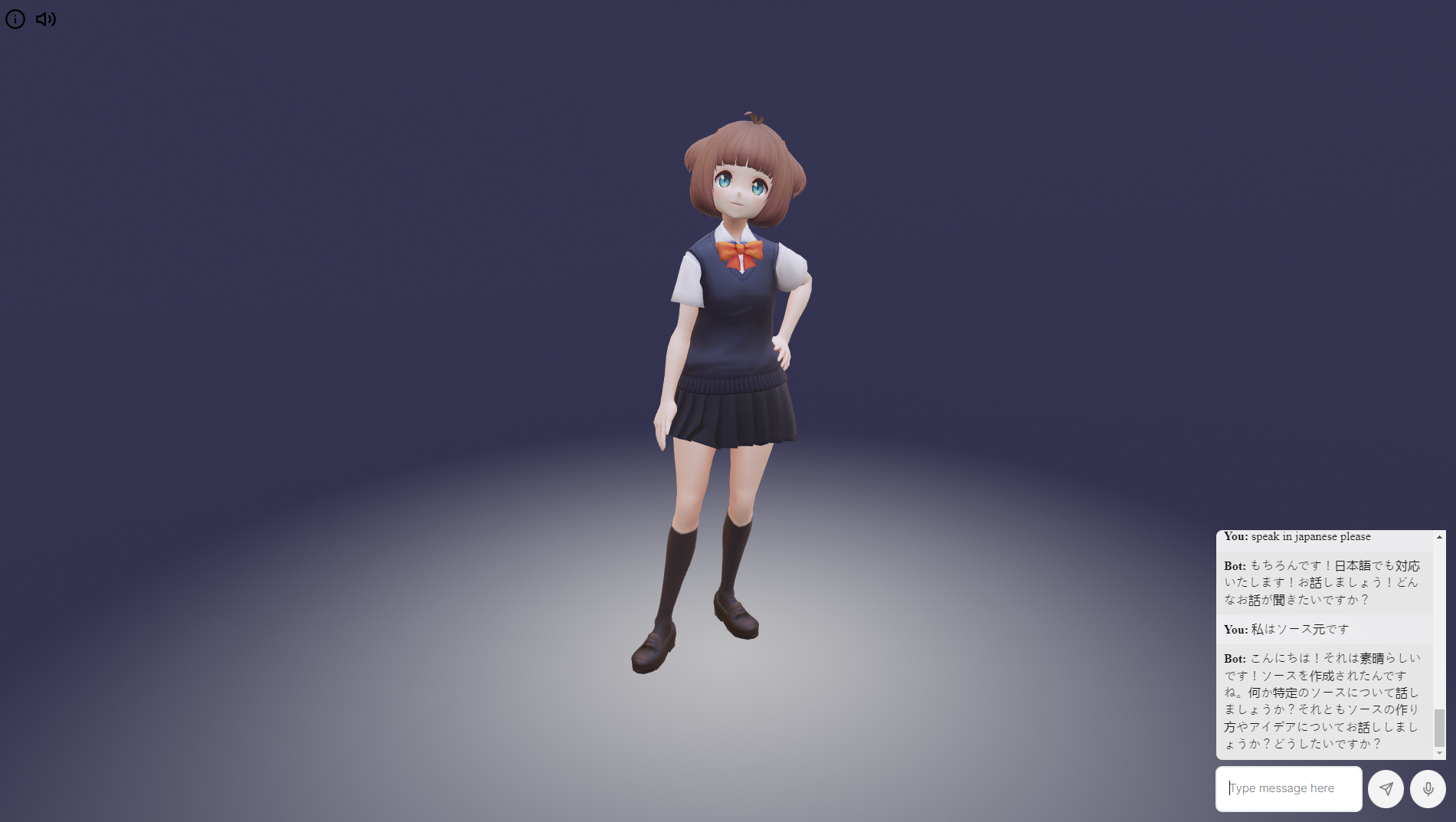

Congratulations! you have created a Multilingual Virtual 3D Assistant with ChatGTP and Google Cloud

Leave a comment