How to run Large Language Model FLAN -T5 and GPT locally
Hello everyone, today we are going to run a Large Language Model (LLM) Google FLAN-T5 locally and GPT2.
When you are building new applications by using LLM and you require a development environment in this tutorial I will explain how to do it.
Introduction

FLAN-T5
FLAN-T5 is a Large Language Model open sourced by Google under the Apache license at the end of 2022. It is available in different sizes - see the model card.
- google/flan-t5-small: 80M parameters; 300 MB download
- google/flan-t5-base: 250M parameters
- google/flan-t5-large: 780M parameters; 1 GB download
- google/flan-t5-xl: 3B parameters; 12 GB download
- google/flan-t5-xxl: 11B parameters
FLAN-T5 models use the following models and techniques:
- The pretrained model T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer)
- The FLAN (Finetuning Language Models) collection to do fine-tuning multiple tasks
GPTNeo
The GPTNeo model was released in the EleutherAI/gpt-neo repository by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy. It is a GPT2 like causal language model trained on the Pile dataset.
Step 1. Installation of Conda
First you need to install anaconda at this link
in this location C:\Anaconda3 , then you, check that your terminal , recognize conda
C:\conda --version
conda 23.1.0
Step 2. Environment creation
The environments supported that I will consider is Python 3.10,
I will create an environment called LLM, but you can put the name that you like.
conda create -n LLM python==3.10
then we activate
conda activate LLM
then in your terminal type the following commands:
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
conda install ipykernel notebook
then
python -m ipykernel install --user --name LLM --display-name "Python (LLM)"
then we can install jupyter lab
pip install jupyterlab
then we install the following libraries used to the creation of our environment
For this
pip install transformers
pip install transformers[torch]
If we have CUDA capability we are going to use CUDA 11.4 and you can download here
pip install torch==1.12.1+cu113 torchvision==0.13.1+cu113 torchaudio==0.12.1 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113
otherwise
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio cpuonly -c pytorch
pip install chardet
pip install fitz
pip install PyMuPDF
conda install -c conda-forge ipywidgets
jupyter nbextension enable --py widgetsnbextension
If you have different versions of CUDA you can install the best version of torch that fit your computer here
we would like to create a folder to work
mkdir workspace && cd workspace
later we open a the jupyter lab
jupyter lab
then you create a new notebook Python (LLM)
Google FLAN-T5
There are different models of FLAN-T5 out there. For this demo we will use the following Google Models:
-
google/flan-t5-small
-
google/flan-t5-large
and from EleutherAI the GPT2 model
- EleutherAI/gpt-neo-125M
Step 3. Large Language Model FLAN-T5 and GTP locally
In this notebook we are going to run different versions of FLAN-T5 and GTP
We define the following prompt:
prompt ="A step by step recipe to make bolognese pasta:"
FLAN-T5-small
Here we are going to download 300 MB of data of the model
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("google/flan-t5-small")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/flan-t5-small")
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(**inputs)
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
['Pour a cup of bolognese into a large bowl and add the pasta']
FLAN-T5-large
Here we are going to download 3GB MB of data of the model
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("google/flan-t5-large")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/flan-t5-large")
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model.generate(**inputs)
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
['Toss the pasta with the sauce, then add the meat and toss again.']
CUDA Capability
import torch
is_cuda=torch.cuda.is_available()
if is_cuda:
print("This computer uses CUDA")
else:
print("This computer uses CPU")
This computer uses CUDA
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/flan-t5-large")
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("google/flan-t5-large").to(device)
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs)
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
['Toss the pasta with the sauce, then add the meat and toss again.']
GPT-neo-125M
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-125M")
model.to(device)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-125M")
input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
#outputs = model.generate(**input_ids)
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids, do_sample=True, max_length=400)
Setting `pad_token_id` to `eos_token_id`:50256 for open-end generation.
generation =tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=False)
print('\n'.join(generation))
We got the following results
A step by step recipe to make bolognese pasta:
Formalizing the ingredients and sauces
Wipe up the ingredients
Wipe the sauce without over or overstitching the ingredients.
FRENCH TENDER
I make a bolognese pasta for a wedding reception, using what I have learned from many other things but one thing about bolognese pasta is that I want a traditional Italian recipe for a wedding. This recipe has an Italian twist:
1/4 ounce Italian sausage cheese
1/4 ounce Italian sausage salt
2/3 ounce Italian sausage fresh ramekins
1/2 ounce Italian sausage chopped onions
1/2 ounce Italian sausage chopped parsley
In a shallow saucepan, melt butter and sauté onion
2/3 ounce Italian sausage with and sauce
salt and pepper
2/3 ounce Italian sausage chopped parsley
Thoroughly sauté onion until it softens
2/3 ounce Italian sausage with and sauce
salt and pepper
Preheat the oven to 325 degrees
Bring a large kettle to 50 to 60°
Sauté onion over medium-high heat
2/3 ounce Italian sausage with and sauce
salt and pepper
In a skillet lightly butter a small pot with 2/3 ounce Italian sauce
salt and pepper
Add 2/3 ounce Italian sauce seasoned with salt, pepper and mix well.
Sift together sausage, seasoning and garlic
Add enough water to bring to boil
Slowly pour in ingredients while stirring
Add enough water to bring to boil
Gravfry the pasta to lightly coat with oil
Place the pasta on the bottom rack with foil
Heat oil in skillet
Oil a small stovetop dish with hot brown sugar
Smoke the sauce. Place your fingers into the meat
sauté onion over hot oven(s)/heat
HuggingFace Enviroment
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
import torch
import gradio as gr
import re
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/flan-t5-large")
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("google/flan-t5-large").to(device)
class GUI:
def query(self,query,tokens=30):
options=""
tok_len=tokens
t5query = f"""Question: "{query}" Context: {options}"""
inputs = tokenizer(t5query, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=tok_len)
return tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
def begin(self,question,tokens):
results = app.query(question,tokens)
return results
app = GUI()
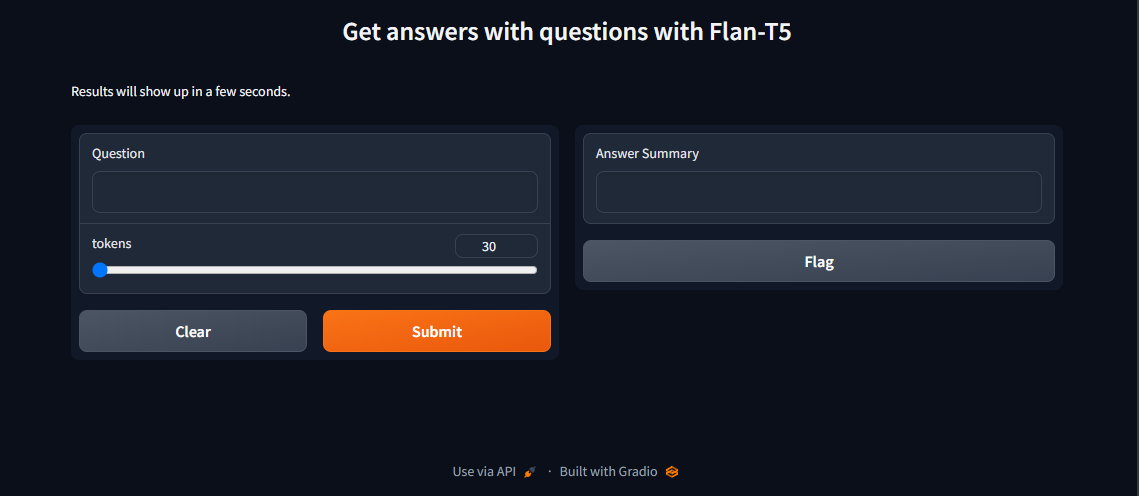
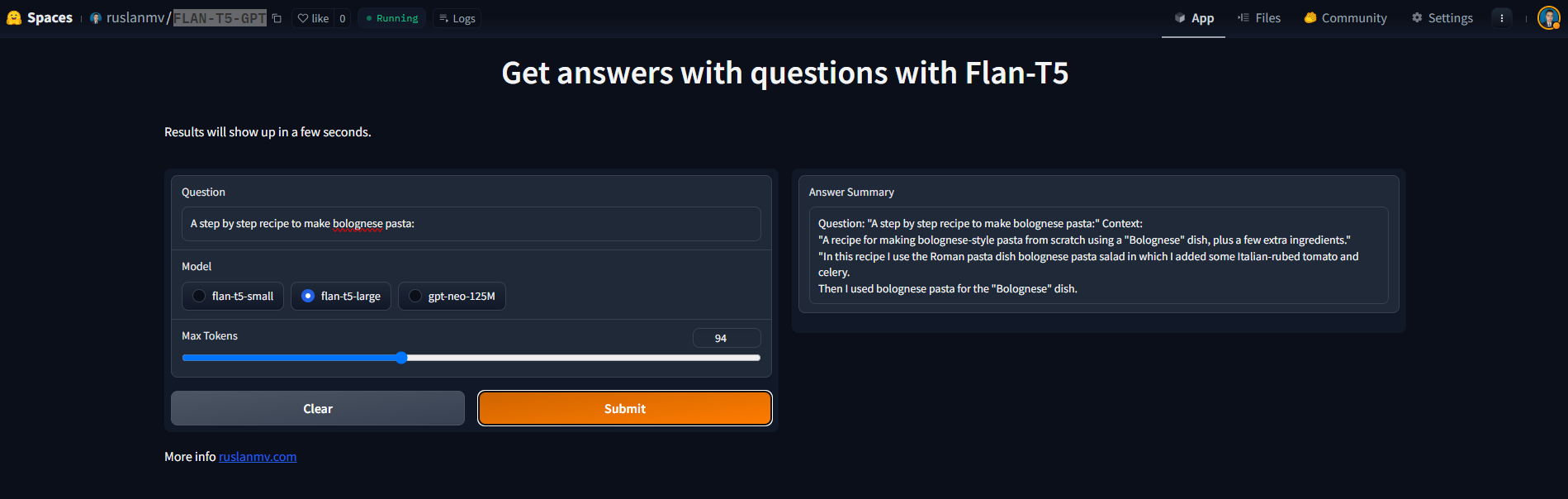
title = "Get answers with questions with Flan-T5"
description = "Results will show up in a few seconds."
css = """.output_image, .input_image {height: 600px !important}"""
iface = gr.Interface(fn=app.begin,
inputs=[ gr.Textbox(label="Question"),
gr.Slider(30, 100, value=30, step = 1)
],
outputs = gr.Text(label="Answer Summary"),
title=title,
description=description,
#article=article,
css=css,
analytics_enabled = True, enable_queue=True)
iface.launch(inline=False, share=False, debug=False)
Running on local URL: http://127.0.0.1:7860
To create a public link, set `share=True` in `launch()`.
iface.launch()
FLAN-T5 vs GTP Neo
Now let us merge all tree models together and check the differences
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
import gradio as gr
import re
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
class GUI:
def query(self,query,modelo="flan-t5-small",tokens=100):
options=""
tok_len=tokens
t5query = f"""Question: "{query}" Context: {options}"""
if (modelo=="flan-t5-small" or modelo=="flan-t5-large"):
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/{}".format(modelo))
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("google/{}".format(modelo)).to(device)
inputs = tokenizer(t5query, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=tok_len)
else:
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-125M").to(device)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neo-125M")
input_ids = tokenizer(t5query, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids, do_sample=True, max_length=tok_len)
generation=tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
return '\n'.join(generation)
def begin(self,question,modelo,tokens):
results = app.query(question,tokens)
return results
app = GUI()
title = "Get answers with questions with Flan-T5"
description = "Results will show up in a few seconds."
article="More info <a href='https://ruslanmv.com/'>ruslanmv.com</a><br>"
css = """.output_image, .input_image {height: 600px !important}"""
iface = gr.Interface(fn=app.begin,
inputs=[ gr.Textbox(label="Question"),
gr.Radio(["flan-t5-small", "flan-t5-large","gpt-neo-125M"],label="Model",value="flan-t5-small"),
gr.Slider(30, 200, value=100, step = 1,label="Max Tokens"),],
outputs = gr.Text(label="Answer Summary"),
title=title,
description=description,
article=article,
css=css,
analytics_enabled = True
,enable_queue=True)
iface.launch(inline=False, share=False, debug=False)
Running on local URL: http://127.0.0.1:7860
To create a public link, set `share=True` in `launch()`.
iface.launch()
You can check out this program in the following link:
https://huggingface.co/spaces/ruslanmv/FLAN-T5-GPT
Uninstall Environment
If you have issues to the installation of the kernel you can remove the kernel and the environment and try again.
To list the kernels currently installed execute
jupyter kernelspec list
To remove a kernel execute
jupyter kernelspec remove LLM
and to remove the environment
conda remove -n llm --all
Congratulations! You have created a web app with Gradio by using LLM Model FLAN-T5 and GPT Neo.
Leave a comment