Data Engineer working in Spark and Python
Hello I have collected some notes about important concepts that every Data Engineer working in Spark should know.
There are almost 100 questions splited in four sections:
- Fundamentals of Apache Spark
- Fundamentals of Databases
- Important concepts in Python
I have collected those questions during my preparation as a Data Engineer.
1. Fundamentals of Apache Spark
What is Apache Spark?
Apache Spark is an open-source cluster computing framework for real-time processing. It has a thriving open-source community and is the most active Apache project at the moment. Spark provides an interface for programming entire clusters with implicit data parallelism and fault-tolerance.
Explain the key features of Apache Spark.
Polyglot Speed Multiple Format Support Lazy Evaluation Real Time Computation Hadoop Integration Machine Learning Let us look at these features in detail:
Polyglot: Spark provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python and R. Spark code can be written in any of these four languages. It provides a shell in Scala and Python. The Scala shell can be accessed through ./bin/spark-shell and Python shell through ./bin/pyspark from the installed directory.
Speed: Spark runs upto 100 times faster than Hadoop MapReduce for large-scale data processing. Spark is able to achieve this speed through controlled partitioning. It manages data using partitions that help parallelize distributed data processing with minimal network traffic.
Multiple Formats: Spark supports multiple data sources such as Parquet, JSON, Hive and Cassandra. The Data Sources API provides a pluggable mechanism for accessing structured data though Spark SQL. Data sources can be more than just simple pipes that convert data and pull it into Spark.
Lazy Evaluation: Apache Spark delays its evaluation till it is absolutely necessary. This is one of the key factors contributing to its speed. For transformations, Spark adds them to a DAG of computation and only when the driver requests some data, does this DAG actually gets executed.
Real Time Computation: Spark’s computation is real-time and has less latency because of its in-memory computation. Spark is designed for massive scalability and the Spark team has documented users of the system running production clusters with thousands of nodes and supports several computational models.
Hadoop Integration: Apache Spark provides smooth compatibility with Hadoop. This is a great boon for all the Big Data engineers who started their careers with Hadoop. Spark is a potential replacement for the MapReduce functions of Hadoop, while Spark has the ability to run on top of an existing Hadoop cluster using YARN for resource scheduling.
Machine Learning: Spark’s MLlib is the machine learning component which is handy when it comes to big data processing. It eradicates the need to use multiple tools, one for processing and one for machine learning. Spark provides data engineers and data scientists with a powerful, unified engine that is both fast and easy to use.
Do you need to install Spark on all nodes of YARN cluster?
No, because Spark runs on top of YARN. Spark runs independently from its installation. Spark has some options to use YARN when dispatching jobs to the cluster, rather than its own built-in manager, or Mesos. Further, there are some configurations to run YARN. They include master, deploy-mode, driver-memory, executor-memory, executor-cores, and queue.
Explain the concept of Resilient Distributed Dataset (RDD).
RDD stands for Resilient Distribution Datasets. An RDD is a fault-tolerant collection of operational elements that run in parallel. The partitioned data in RDD is immutable and distributed in nature.
RDDs are basically parts of data that are stored in the memory distributed across many nodes. RDDs are lazily evaluated in Spark. This lazy evaluation is what contributes to Spark’s speed.
How do we create RDDs in Spark?
Spark provides two methods to create RDD: 1. By parallelizing a collection in your Driver program. 2. This makes use of SparkContext’s ‘parallelize’ method
val DataArray = Array(2,4,6,8,10)
val DataRDD = sc.parallelize(DataArray)
Define Partitions in Apache Spark.
As the name suggests, partition is a smaller and logical division of data similar to ‘split’ in MapReduce. It is a logical chunk of a large distributed data set. Partitioning is the process to derive logical units of data to speed up the processing process. Spark manages data using partitions that help parallelize distributed data processing with minimal network traffic for sending data between executors. By default, Spark tries to read data into an RDD from the nodes that are close to it. Since Spark usually accesses distributed partitioned data, to optimize transformation operations it creates partitions to hold the data chunks. Everything in Spark is a partitioned RDD.
What operations does RDD support?
RDDs support two types of operations: transformations and actions. Transformations: Transformations create new RDD from existing RDD like map, reduceByKey and filter we just saw. Transformations are executed on demand. That means they are computed lazily. Actions: Actions return final results of RDD computations. Actions triggers execution using lineage graph to load the data into original RDD, carry out all intermediate transformations and return final results to Driver program or write it out to file system.
What do you understand by Transformations in Spark?
Transformations are functions applied on RDD, resulting into another RDD. It does not execute until an action occurs. map() and filter() are examples of transformations, where the former applies the function passed to it on each element of RDD and results into another RDD. The filter() creates a new RDD by selecting elements from current RDD that pass function argument.
val rawData=sc.textFile("path to/movies.txt")
val moviesData=rawData.map(x=>x.split(" "))
Define Actions in Spark.
An action helps in bringing back the data from RDD to the local machine. An action’s execution is the result of all previously created transformations. Actions triggers execution using lineage graph to load the data into original RDD, carry out all intermediate transformations and return final results to Driver program or write it out to file system. reduce() is an action that implements the function passed again and again until one value if left. take() action takes all the values from RDD to a local node.
Name the components of Spark Ecosystem.
Spark Core: Base engine for large-scale parallel and distributed data processing Spark Streaming: Used for processing real-time streaming data Spark SQL: Integrates relational processing with Spark’s functional programming API GraphX: Graphs and graph-parallel computation MLlib: Performs machine learning in Apache Spark
What is a Parquet file?
Parquet is a columnar format file supported by many other data processing systems. Spark SQL performs both read and write operations with Parquet file and consider it be one of the best big data analytics formats so far. Parquet is a columnar format, supported by many data processing systems. The advantages of having a columnar storage are as follows: Columnar storage limits IO operations. It can fetch specific columns that you need to access. Columnar storage consumes less space. It gives better-summarized data and follows type-specific encoding.
What file systems does Spark support?
The following three file systems are supported by Spark: Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). Local File system. Amazon S3
What do you understand by worker node?
Worker node refers to any node that can run the application code in a cluster. The driver program must listen for and accept incoming connections from its executors and must be network addressable from the worker nodes. Worker node is basically the slave node. Master node assigns work and worker node actually performs the assigned tasks. Worker nodes process the data stored on the node and report the resources to the master. Based on the resource availability, the master schedule tasks.
What are broadcast variables?
Broadcast variables allow the programmer to keep a read-only variable cached on each machine rather than shipping a copy of it with tasks. They can be used to give every node a copy of a large input dataset in an efficient manner. Spark also attempts to distribute broadcast variables using efficient broadcast algorithms to reduce communication cost.
Explain accumulators in Apache Spark.
Accumulators are variables that are only added through an associative and commutative operation. They are used to implement counters or sums. Tracking accumulators in the UI can be useful for understanding the progress of running stages. Spark natively supports numeric accumulators. We can create named or unnamed accumulators.
Why is there a need for broadcast variables when working with Apache Spark?
Broadcast variables are read only variables, present in-memory cache on every machine. When working with Spark, usage of broadcast variables eliminates the necessity to ship copies of a variable for every task, so data can be processed faster. Broadcast variables help in storing a lookup table inside the memory which enhances the retrieval efficiency when compared to an RDD lookup().
What are the various data sources available in Spark SQL?
Parquet file, JSON datasets and Hive tables are the data sources available in Spark SQL.
What do you understand by Lazy Evaluation?
Spark is intellectual in the manner in which it operates on data. When you tell Spark to operate on a given dataset, it heeds the instructions and makes a note of it, so that it does not forget – but it does nothing, unless asked for the final result. When a transformation like map() is called on an RDD, the operation is not performed immediately. Transformations in Spark are not evaluated till you perform an action. This helps optimize the overall data processing workflow.
How is Apache Spark different from MapReduce?
Spark processes data in batches as well as in real-time
MapReduce processes data in batches only
Spark runs almost 100 times faster than Hadoop MapReduce
Hadoop MapReduce is slower when it comes to large scale data processing
Spark stores data in the RAM i.e. in-memory. So, it is easier to retrieve it
Hadoop MapReduce data is stored in HDFS and hence takes a long time to retrieve the data
Spark provides caching and in-memory data storage
Hadoop is highly disk-dependent
What is shuffling in Spark? When does it occur?
Shuffling is the process of redistributing data across partitions that may lead to data movement across the executors. The shuffle operation is implemented differently in Spark compared to Hadoop. Shuffling has 2 important compression parameters: spark.shuffle.compress – checks whether the engine would compress shuffle outputs or not spark.shuffle.spill.compress – decides whether to compress intermediate shuffle spill files or not It occurs while joining two tables or while performing byKey operations such as GroupByKey or ReduceByKey
What is the use of coalesce in Spark?
Spark uses a coalesce method to reduce the number of partitions in a DataFrame. Suppose you want to read data from a CSV file into an RDD having four partitions. partition This is how a filter operation is performed to remove all the multiple of 10 from the data. The RDD has some empty partitions. It makes sense to reduce the number of partitions, which can be achieved by using coalesce.
How do you convert a Spark RDD into a DataFrame?
There are 2 ways to convert a Spark RDD into a DataFrame: Using the helper function - toDF
import com.mapr.db.spark.sql._
val df = sc.loadFromMapRDB(<table-name>) .where(field(“first_name”) === “Peter”) .select(“_id”, “first_name”).toDF()
Using SparkSession.createDataFrame You can convert an RDD[Row] to a DataFrame by calling createDataFrame on a SparkSession object def createDataFrame(RDD, schema:StructType)
Explain the types of operations supported by RDDs.
RDDs support 2 types of operation: Transformations: Transformations are operations that are performed on an RDD to create a new RDD containing the results (Example: map, filter, join, union) Actions: Actions are operations that return a value after running a computation on an RDD (Example: reduce, first, count)
Explain Caching in Spark Streaming.
Caching also known as Persistence is an optimization technique for Spark computations. Similar to RDDs, DStreams also allow developers to persist the stream’s data in memory. That is, using the persist() method on a DStream will automatically persist every RDD of that DStream in memory. It helps to save interim partial results so they can be reused in subsequent stages.
What is the need for broadcast variables in Spark?
Broadcast variables allow the programmer to keep a read-only variable cached on each machine rather than shipping a copy of it with tasks. They can be used to give every node a copy of a large input dataset in an efficient manner. Spark distributes broadcast variables using efficient broadcast algorithms to reduce communication costs.
scala scala> val broadcastVar = sc.broadcast(Array(1, 2, 3))
broadcastVar: org.apache.spark.broadcast.Broadcast[Array[Int]] = Broadcast(0)
scala> broadcastVar.value res0: Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3)
What are the functions of Spark SQL?
Spark SQL is Apache Spark’s module for working with structured data. Spark SQL loads the data from a variety of structured data sources. It queries data using SQL statements, both inside a Spark program and from external tools that connect to Spark SQL through standard database connectors (JDBC/ODBC). It provides a rich integration between SQL and regular Python/Java/Scala code, including the ability to join RDDs and SQL tables and expose custom functions in SQL.
How can you connect Hive to Spark SQL?
To connect Hive to Spark SQL, place the hive-site.xml file in the conf directory of Spark. hive-spark Using the Spark Session object, you can construct a DataFrame. result=spark.sql(“select * from
How can you manipulate structured data using domain-specific language in Spark SQL?
Structured data can be manipulated using domain-Specific language as follows:
Suppose there is a DataFrame with the following information:
val df = spark.read.json("examples/src/main/resources/people.json")
// Displays the content of the DataFrame to stdout
df.show()
// +----+-------+
// | age| name|
// +----+-------+
// |null|Michael|
// | 30| Andy|
// | 19| Justin|
// +----+-------+
// Select only the "name" column
df.select("name").show()
// +-------+
// | name|
// +-------+
// |Michael|
// | Andy|
// | Justin|
// +-------+
// Select everybody, but increment the age by 1
df.select($"name", $"age" + 1).show()
// +-------+---------+
// | name|(age + 1)|
// +-------+---------+
// |Michael| null|
// | Andy| 31|
// | Justin| 20|
// +-------+---------+
// Select people older than 21
df.filter($"age" > 21).show()
// +---+----+
// |age|name|
// +---+----+
// | 30|Andy|
// +---+----+
// Count people by age
df.groupBy("age").count().show()
// +----+-----+
// | age|count|
// +----+-----+
// | 19| 1|
// |null| 1|
// | 30| 1|
// +----+-----+
What is Dataframe in Spark in few words
Distributed collection of data organized into named columns. Data organized into named columns.
For example a table in a relational database. It is an immutable distributed collection of data.
What is Dataset in spark
Its an extension of Dataframe API but optimized. A Dataset is a strongly typed collection of domain-specific objects that can be transformed in parallel using functional or relational operations.
Each Dataset also has an untyped view called a DataFrame, which is a Dataset of Row.
What is RDD
A Resilient Distributed Dataset is an immutable collection of objects (can be any from Python, Java or Scala). There are 2 ways to create them:
- Parallelizing an existing collection in your program;
- Referencing a dataset available in HDFS.
The key idea of spark is Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDD); it supports in-memory processing computation. This means, it stores the state of memory as an object across the jobs and the object is sharable between those jobs. It will store intermediate results in a distributed memory instead of Stable storage (Disk) and make the system faster.
What is Shuffling
The Spark SQL shuffle is a mechanism for redistributing or re-partitioning data. You can change the spark.sql.shuffle.partitions configuration to increase the number of them. When you have some performance losses they can be caused by shuffling as it moves the data between worker nodes. It usually triggers when performing operations like: groupByKey(), reducebyKey(), join().
Spark first runs map tasks on all partitions which groups all values for a single key. The results of the map tasks are kept in memory. When results do not fit in memory, Spark stores the data into a disk.
Spark shuffles the mapped data across partitions, some times it also stores the shuffled data into a disk for reuse when it needs to recalculate. Run the garbage collection. Finally runs reduce tasks on each partition based on key.
2. Fundamentals of Databases
What is a Database?
Database is nothing but an organized form of data for easy access, storing, retrieval and managing of data. This is also known as structured form of data which can be accessed in many ways. Example: School Management Database, Bank Management Database.
What is a primary key?
A primary key is a combination of fields which uniquely specify a row. This is a special kind of unique key, and it has implicit NOT NULL constraint. It means, Primary key values cannot be NULL.
What is a unique key?
A Unique key constraint uniquely identified each record in the database. This provides uniqueness for the column or set of columns. A Primary key constraint has automatic unique constraint defined on it. But not, in the case of Unique Key. There can be many unique constraint defined per table, but only one Primary key constraint defined per table.
What is a foreign key?
A foreign key is one table which can be related to the primary key of another table. Relationship needs to be created between two tables by referencing foreign key with the primary key of another table.
What is a join?
This is a keyword used to query data from more tables based on the relationship between the fields of the tables. Keys play a major role when JOINs are used.
What are the types of join and explain each?
There are various types of join which can be used to retrieve data and it depends on the relationship between tables.
Inner Join. Inner join return rows when there is at least one match of rows between the tables.
Right Join. Right join return rows which are common between the tables and all rows of Right hand side table. Simply, it returns all the rows from the right hand side table even though there are no matches in the left hand side table.
Left Join. Left join return rows which are common between the tables and all rows of Left hand side table. Simply, it returns all the rows from Left hand side table even though there are no matches in the Right hand side table.
Full Join. Full join return rows when there are matching rows in any one of the tables. This means, it returns all the rows from the left hand side table and all the rows from the right hand side table.
What is a View?
A view is a virtual table which consists of a subset of data contained in a table. Views are not virtually present, and it takes less space to store. View can have data of one or more tables combined, and it is depending on the relationship.
What is an Index?
An index is performance tuning method of allowing faster retrieval of records from the table. An index creates an entry for each value and it will be faster to retrieve data.
What are all the different types of indexes?
There are three types of indexes -.
Unique Index. This indexing does not allow the field to have duplicate values if the column is unique indexed. Unique index can be applied automatically when primary key is defined.
Clustered Index. This type of index reorders the physical order of the table and search based on the key values. Each table can have only one clustered index
NonClustered Index. NonClustered Index does not alter the physical order of the table and maintains logical order of data. Each table can have 999 nonclustered indexes.
What is a Cursor?
A database Cursor is a control which enables traversal over the rows or records in the table. This can be viewed as a pointer to one row in a set of rows. Cursor is very much useful for traversing such as retrieval, addition and removal of database records.
What is a trigger?
A DB trigger is a code or programs that automatically execute with response to some event on a table or view in a database. Mainly, trigger helps to maintain the integrity of the database. Example: When a new student is added to the student database, new records should be created in the related tables like Exam, Score and Attendance tables.
What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE commands?
DELETE command is used to remove rows from the table, and WHERE clause can be used for conditional set of parameters. Commit and Rollback can be performed after delete statement.
TRUNCATE removes all rows from the table. Truncate operation cannot be rolled back.
What is a constraint?
Constraint can be used to specify the limit on the data type of table. Constraint can be specified while creating or altering the table statement. Sample of constraint are.
NOT NULL.
CHECK.
DEFAULT.
UNIQUE.
PRIMARY KEY.
FOREIGN KEY.
What is data Integrity?
Data Integrity defines the accuracy and consistency of data stored in a database. It can also define integrity constraints to enforce business rules on the data when it is entered into the application or database.
What is Datawarehouse?
Datawarehouse is a central repository of data from multiple sources of information. Those data are consolidated, transformed and made available for the mining and online processing. Warehouse data have a subset of data called Data Marts.
What is collation?
Collation is defined as set of rules that determine how character data can be sorted and compared. This can be used to compare A and, other language characters and also depends on the width of the characters.
What is Online Transaction Processing (OLTP)?
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) manages transaction based applications which can be used for data entry, data retrieval and data processing. OLTP makes data management simple and efficient. Unlike OLAP systems goal of OLTP systems is serving real-time transactions. Example – Bank Transactions on a daily basis.
What is CLAUSE?
SQL clause is defined to limit the result set by providing condition to the query. This usually filters some rows from the whole set of records. Example – Query that has WHERE condition Query that has HAVING condition.
What is Union, minus and Interact commands?
UNION operator is used to combine the results of two tables, and it eliminates duplicate rows from the tables.
MINUS operator is used to return rows from the first query but not from the second query. Matching records of first and second query and other rows from the first query will be displayed as a result set.
INTERSECT operator is used to return rows returned by both the queries.
What is the difference between TRUNCATE and DROP statements?
TRUNCATE removes all the rows from the table, and it cannot be rolled back. DROP command removes a table from the database and operation cannot be rolled back.
What are aggregate and scalar functions?
Aggregate functions are used to evaluate mathematical calculation and return single values. This can be calculated from the columns in a table. Scalar functions return a single value based on the input value.
Example -.
Aggregate – max(), count - Calculated with respect to numeric.
Scalar – UCASE(), NOW() – Calculated with respect to strings.
How to fetch common records from two tables?
Select studentID from student INTERSECT Select StudentID from Exam
How to fetch alternate records from a table?
records can be fetched for both Odd and Even row numbers -.
To display even numbers-.
Select studentId from (Select rowno, studentId from student) where mod(rowno,2)=0
To display odd numbers
Select studentId from (Select rowno, studentId from student) where mod(rowno,2)=1
How to select unique records from a table?
Select unique records from a table by using DISTINCT keyword.
Select DISTINCT StudentID, StudentName from Student.
What is the command used to fetch first 5 characters of the string?
There are many ways to fetch first 5 characters of the string -.
Select SUBSTRING(StudentName,1,5) as studentname from student
Select LEFT(Studentname,5) as studentname from student
What is a Builder ?
Builder is a creational design pattern, which allows constructing complex objects step by step. Unlike other creational patterns, Builder doesn’t require products to have a common interface. That makes it possible to produce different products using the same construction process.
What are the structured of data?
Structured data is most often categorized as quantitative data, and it’s the type of data most of us are used to working with. Think of data that fits neatly within fixed fields and columns in relational databases and spreadsheets. Examples of structured data include names, dates, addresses, credit card numbers, stock information, geolocation, and more. The programming language used for managing structured data is called structured query language, also known as SQL.
Data structures are the means by which you can input and organize data in order to do something with it.
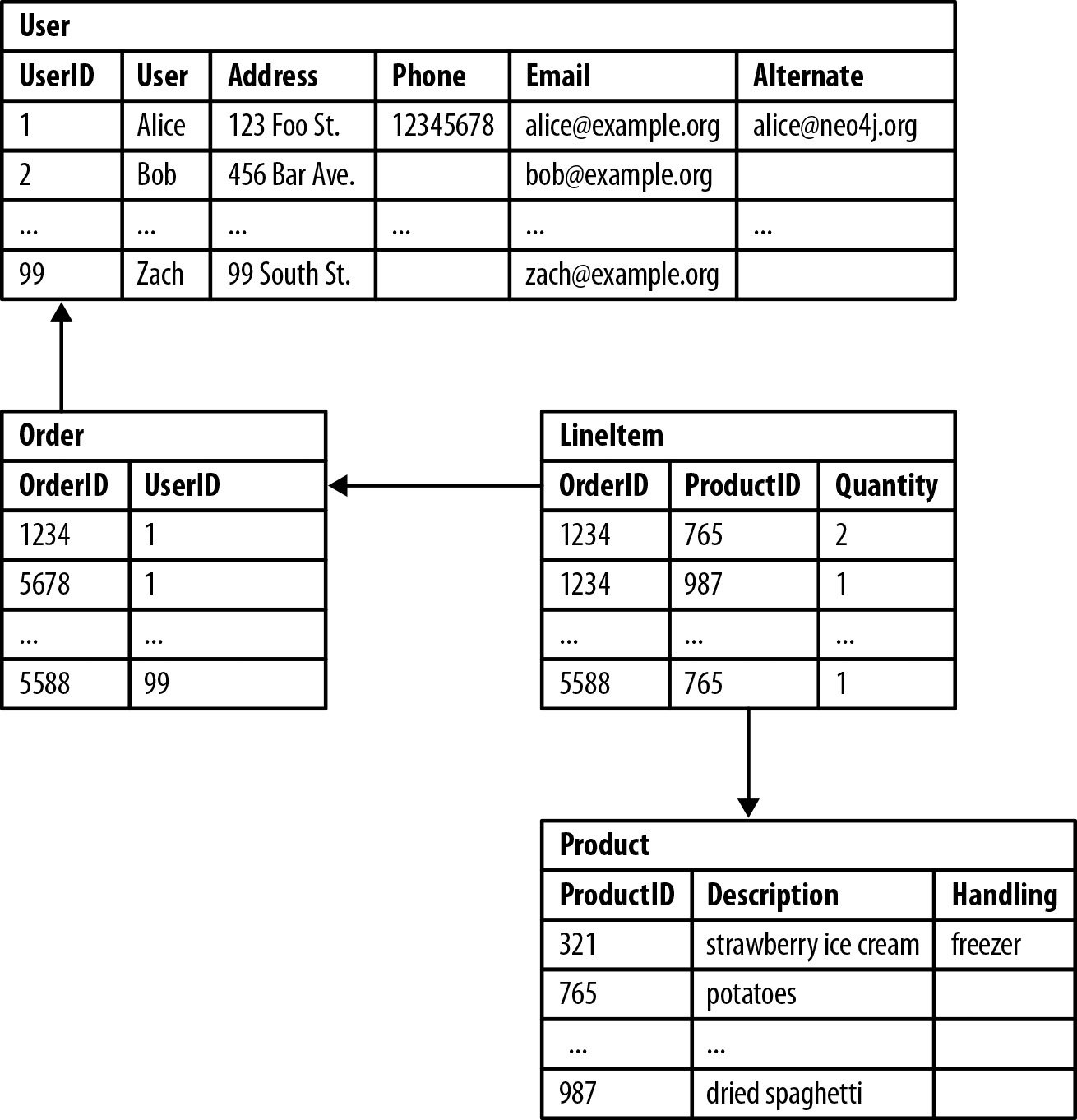
What is the difference between relational and non relational database?
Unstructured data is most often categorized as qualitative data, and it cannot be processed and analyzed using conventional data tools and methods. Examples of unstructured data include text, video files, audio files, mobile activity, social media posts, satellite imagery, surveillance imagery – the list goes on and on.
Unstructured data is difficult to deconstruct because it has no predefined data model, meaning it cannot be organized in relational databases. Instead, non-relational or NoSQL databases are the best fit for managing unstructured data.
| Structured data | Unstructured data |
|---|---|
| Structured data is quantitative data that consists of numbers and values. | Unstructured data is qualitative data that consists of audio, video, sensors, descriptions, and more. |
| Structured data is used in machine learning and drives machine learning algorithms. | Unstructured data is used in natural language processing and text mining. |
| Structured data is stored in tabular formats like excel sheets or SQL databases. | Stored as audio files, videos files, or NoSQL databases |
| Structured data has a pre-defined data model. | Unstructured data does not have a pre-defined data model. |
| Structured data is sourced from online forms, GPS sensors, network logs, web server logs, OLTP systems, and the like. | Unstructured data is sourced from email messages, word-processing documents, pdf files, and so on. |
| Structured data is stored in data warehouses | Unstructured data is stored in data lakes |
| Structured data requires less storage space and is highly scalable. | Unstructured data requires more storage space and is difficult to scale. |
Difference between Schema and Instance?
The main difference between schema and instance is that a schema is a structural view of the database, while the instance is the data stored in a database at a particular moment of time.
The data stored in database at a particular moment of time is called instance of database
What is Query builder?
Query Builder enables you to select data from the database based on one or more conditions.
Some SQL query builders
| Name | Supported platforms | Database | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| DbVisualizer | Windows, Linux, and macOS | SQL Server, Oracle, MYSQL,PostgreSQL, SQLite etc | Learn More |
| SQL Prompt | Windows 10. Windows 8. Windows Server 2019. | SQL Server, Oracle, and MYSQL. | Learn More |
| Active Query Builder | Mac and Windows. | SQL Server, SQLite, IBM, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Sybase, etc. | Learn More |
| Devart | Windows and Mac. | SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL | Learn More |
| Aquafold | Linux, macOS, and Windows. | Apache Cassandra, IBM Netezza, Amazon Redshift, Oracle, and MySQL databases. | Learn More |
Example
What is Yarn?
YARN is an Apache Hadoop technology and stands for Yet Another Resource Negotiator. YARN is a large-scale, distributed operating system for big data applications. The technology is designed for cluster management and is one of the key features in the second generation of Hadoop. YARN is a software rewrite that is capable of decoupling MapReduce’s resource management and scheduling capabilities from the data processing component.
YARN is a distributed container manager, like Mesos for example, whereas Spark is a data processing tool. Spark can run on YARN, the same way Hadoop Map Reduce can run on YARN. Running Spark on YARN necessitates a binary distribution of Spark as built on YARN support.
What is MapReduce?
MapReduce is a software framework and programming model used for processing huge amounts of data. MapReduce program work in two phases, namely:
Map and Reduce.
Map tasks deal with splitting and mapping of data while Reduce tasks shuffle and reduce the data.

What is Hbase?
HBase is a column-oriented non-relational database management system that runs on top of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). HBase provides a fault-tolerant way of storing sparse data sets, which are common in many big data use cases. It is well suited for real-time data processing or random read/write access to large volumes of data.
What is Apache Kafka ?
Apache Kafka is a framework implementation of a software bus using stream-processing. It is an open-source software platform developed by the Apache Software Foundation written in Scala and Java. The project aims to provide a unified, high-throughput, low-latency platform for handling real-time data feeds. Kafka can connect to external systems (for data import/export) via Kafka Connect and provides Kafka Streams, a Java stream processing library. Kafka uses a binary TCP-based protocol that is optimized for efficiency and relies on a “message set” abstraction that naturally groups messages together to reduce the overhead of the network roundtrip.
What is Docker ?
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications.
Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly.
Its primary focus is to automate the deployment of applications inside software containers and the automation of operating system level virtualization on Linux
At the writing time of this blog the latest version Docker Engine is 19.03
What are the Docker container states? Created Running ,Paused, Restarting
And the standard states are:
- Create container. Create a container to run it later on with required image. …
- Run docker container.
- Run the docker container with the required image and specified command / process.
- Pause container.
- Unpause container.
- Start container.
- Stop container.
- Restart container
- Kill container.
What is Apache Airflow ?
Apache Airflow is a workflow automation and scheduling system that can be used to author and manage data pipelines. Airflow uses workflows made of directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) of tasks.
A DAG is a construct of nodes and connectors (also called “edges”) where the connectors have direction, and you can start at any arbitrary node to travel through all connectors.
What are the BigQuery Best Practices ?
BigQuery Best Practices:
-
Reduce the amount of data that is needed in the query to the one, you actually need (avoid for example select *);
-
Use the query execution plant and timeline details to look for points for improvement. Query plans are represented as a list of query stages and each stage shows an overview on statistics such as step information (the operation performaed like a JOIN), timing (average and worst-case worker scenario) and classification;
-
Reducing the amoung of bytes shuffled bettwen intermidiate stages –> the amount of data that the query passes to the next stage;
-
CPU required for the query execution;
-
Bytes written in output (final or intermidiate shuffling);
-
Query patterns and best practices:
-
- Avoid
JOIN –> Use Window Functions;
- Filter you data as early as possible;
- Avoid CROSS JOIN (cartesian product) –> pre-aggregate your data with GROUP BY and if possible use a Window Function.
-
Use Buld DML operations instead of point-specific ones.
- Partition data by time and use clustering (determines the sort order of the data)
What are the possible BigQuery Optimizations?
- Avoid SELECT *, instead use column names and select only the needed columns;
- Avoid Distinct clause instead add more primary key columns to the list;
- Avoid Using UNION instead use UNION ALL;
- Avoid using the HAVING after grouping, instead use the WHERE before the grouping;
- Avoid using functions in predicates instead use functions at the right side of the operator;
- Avoid using IN instead use EXISTS;
2. Important concepts in Python
What is coding standard PEP-8?
It describes the rules for writing a beautiful and readable Python code
-
Use 4-space indentation and no tabs.
# Aligned with opening delimiter. grow = function_name(variable_one, variable_two, variable_three, variable_four) -
Use docstrings
def exam(): """This is single line docstring""" """This is a multiline comment""" -
Wrap lines so that they don’t exceed 79 characters
-
Use of regular and updated comments are valuable to both the coders and users
rus= rus + 1 # Increment -
Use of trailing commas
tup = ("ruslanmv",) -
Use Python’s default UTF-8 or ASCII encodings and not any fancy encodings
-
Use spaces around operators and after commas, but not directly inside bracketing constructs:
a = f(1, 2) + g(3, 4) -
Naming Conventions
b (single lowercase letter) B (single upper case letter) lowercase lower_case_with_underscores UPPERCASE UPPER_CASE_WITH_UNDERSCORES CapitalizedWords (or CamelCase). This is also sometimes known as StudlyCaps. Note: While using abbreviations in CapWords, capitalize all the letters of the abbreviation. Thus HTTPServerError is better than HttpServerError. mixedCase (differs from CapitalizedWords by initial lowercase character!) Capitalized_Words_With_Underscores- Name your classes and functions consistently .
- Don’t use non-ASCII characters in identifiers
- Characters that should not be used for identifiers
What are the key features of Python?
Python is well suited to object orientated programming in that it allows the definition of classes along with composition and inheritance. Python does not have access specifiers (like C++’s public, private).
What is Virtual environment?
A virtual environment is a Python environment such that the Python interpreter, libraries and scripts installed into it are isolated from those installed in other virtual environments, and (by default) any libraries installed in a “system” Python, i.e., one which is installed as part of your operating system.
What are tuples in Python?
Tuples are used to store multiple items in a single variable.
mytuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
A tuple is a collection which is ordered and unchangeable.
What is the difference between mutable and not mutable.
A mutable object can be changed after it’s created, and an immutable object can’t.
Tuples are immutable:
# Python code to test that
# tuples are immutable
tuple1 = (0, 1, 2, 3)
tuple1[0] = 4
print(tuple1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "e0eaddff843a8695575daec34506f126.py", line 3, in
tuple1[0]=4
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
Strings are immutable:
# Python code to test that
# strings are immutable
message = "a,b,c,d"
>>> message[0]
'a'
message[0] = '1'
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment
List are mutables
# Python code to test that
# list are mutable
message = [1,2,3,4]
>>> message[0]
1
message[0] = 5
>>> print(message)
[5, 2, 3, 4]
What is the difference between list and tuples in Python?
Lists are mutable i.e they can be edited.
list_1 = [10, ‘Chelsea’, 20]
Lists are slower than tuples.
Tuples are immutable (tuples are lists which can’t be edited).
tup_1 = (10, ‘Chelsea’ , 20)
What is lambda function in Python?
A Lambda Function in Python programming is an anonymous function or a function having no name. It is a small and restricted function having no more than one line
# Program to show the use of lambda functions
double = lambda x: x * 2
print(double(5))
What is decorator in Python?
A decorator in Python is a function that takes another function as its argument, and returns yet another function .
Example, by defining a wrapper inside an enclosed function.
def uppercase_decorator(function):
def wrapper():
func = function()
make_uppercase = func.upper()
return make_uppercase
return wrapper
Our decorator function takes a function as an argument, and we shall, therefore, define a function and pass it to our decorator. We learned earlier that we could assign a function to a variable. We’ll call our decorator function.
def say_hi():
return 'hello there'
decorate = uppercase_decorator(say_hi)
decorate()
'HELLO THERE'
However, Python provides a much easier way for us to apply decorators. We simply use the @ symbol before the function we’d like to decorate. Let’s show that in practice below.
@uppercase_decorator
def say_hi():
return 'hello there'
say_hi()
'HELLO THERE'
What type is function range() in Python?
Python 3 added a new range class to efficiently handle “an immutable sequence of numbers”. The type is <class ‘range’>
What is a class in Python?
Like function definitions begin with the def keyword in Python, class definitions begin with a class keyword.
A class creates a new local namespace where all its attributes are defined. Attributes may be data or functions.
This class object allows us to access the different attributes as well as to instantiate new objects of that class.
class Person:
"This is a person class"
age = 10
def greet(self):
print('Hello')
# Output: 10
print(Person.age)
10
What is object in Python?
Python is an object oriented programming language.
Almost everything in Python is an object, with its properties and methods.
# create a new object of Person class
alex= Person()
# Calling object's greet() method
alex.greet()
Hello
What is self in Python?
Self represents the instance of the class. By using the “self” keyword we can access the attributes and methods of the class in python. It binds the attributes with the given arguments. Example:
class car():
# init method or constructor
def __init__(self, model, color):
self.model = model
self.color = color
def show(self):
print("Model is", self.model )
print("color is", self.color )
# both objects have different self which
# contain their attributes
audi = car("audi a4", "blue")
ferrari = car("ferrari 488", "green")
audi.show() # same output as car.show(audi)
ferrari.show() # same output as car.show(ferrari)
# Behind the scene, in every instance method
# call, python sends the instances also with
# that method call like car.show(audi)
Output
Model is audi a4
color is blue
Model is ferrari 488
color is green
What is Inheritance?
It refers to defining a new class with little or no modification to an existing class.
class BaseClass: #parent
Body of base class
class DerivedClass(BaseClass): #child
Body of derived class
What is Multiple Inheritance
In multiple inheritance, the features of all the base classes are inherited into the derived class.
class Base1:
pass
class Base2:
pass
class MultiDerived(Base1, Base2):
pass
What is Data encapsulation?
Data Encapsulation is an Object Oriented Programming concept that bind a group of related properties, functions, and other members are treated as a single unit.
class Car:
def __init__(self):
self.__updateSoftware()
def drive(self):
print('driving')
def __updateSoftware(self):
print('updating software')
redcar = Car()
redcar.drive()
updating software
driving
What is polymorphism ?
In Python, Polymorphism lets us define methods in the child class that have the same name as the methods in the parent class. In inheritance, the child class inherits the methods from the parent class.
class USA():
def capital(self):
print("Washington, D.C. is the capital of USA.")
def language(self):
print("English is the primary language of USA.")
def type(self):
print("USA is a developed country.")
def func(obj):
obj.capital()
obj.language()
obj.type()
obj_usa = USA()
func(obj_usa)
Output:
Washington, D.C. is the capital of USA.
English is the primary language of USA.
USA is a developed country.
How to pass object of the class as parameter in Python?
Let us consider two classes Person and MyClass, object of class Person is passed as parameter to the method of class MyClass.
class MyClass():
def my_method(self, obj):
print('In my_method method of MyClass')
print("Name:", obj.name)
print("Age:", obj.age)
In MyClass there is one method my_method which takes one more argument apart from self.
from MyClass import MyClass
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
print('init called')
self.name = name
self.age = age
def display(self):
print('in display')
print("Name-", self.name)
print("Age-", self.age)
# object of class MyClass
obj = MyClass()
# passing person object to
# method of MyClass (self = person here)
obj.my_method(self)
person = Person('Ruslan', 35)
person.display()
In class Person, MyClass is also used so that is imported.
from MyClass import MyClass
In method display() object of MyClass is created.
obj = MyClass()
Then the my_method() method of class MyClass is called and object of Person class is passed as parameter.
# passing person object to
# method of MyClass (self = person here)
obj.my_method(self)
On executing this Python program you get output as following.
init called
in display
Name- Ruslan
Age- 35
In my_method method of MyClass
Name: Ruslan
Age: 35
What is a Design Pattern?
A design pattern is a particular approach to solving a recurring problem in software development and is also used to represent good practices.
It represents a particular way of organizing code to produce the desired solution in a recommended way
What is singleton Pattern?
A Singleton pattern in python is a design pattern that allows you to create just one instance of a class, throughout the lifetime of a program.
This pattern restricts the number of objects that can be created from a class to one single object that will often-times be shared globally in an application.
class SingletonClass(object):
def __new__(cls):
if not hasattr(cls, 'instance'):
cls.instance = super(SingletonClass, cls).__new__(cls)
return cls.instance
singleton = SingletonClass()
new_singleton = SingletonClass()
print(singleton is new_singleton)
singleton.singl_variable = "Singleton Variable"
print(new_singleton.singl_variable)
What is decorator in python?
The decorator in Python’s meta-programming is a particular form of a function that takes functions as input and returns a new function as output.
Examples
-
@classmethod
-
@staticmethod
-
@property
import time
from functools import wraps
def karltime(func):
#Decorator for reporting the execution time.
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
end = time.time()
print(func.__name__, end-start)
return result
return wrapper
Here is a program (connected with the previous program) segment that is using a simple decorator
@karltime
def countdown(n):
while n > 0:
n -= 1
What is type conversion in Python?
Ans: Type conversion refers to the conversion of one data type iinto another.
int() – converts any data type into integer type
float() – converts any data type into float type
ord() – converts characters into integer
hex() – converts integers to hexadecimal
oct() – converts integer to octal
tuple() – This function is used to convert to a tuple.
set() – This function returns the type after converting to set.
list() – This function is used to convert any data type to a list type.
dict() – This function is used to convert a tuple of order (key,value) into a dictionary.
str() – Used to convert integer into a string
What is the difference between Python Arrays and lists?
Arrays and lists, in Python, have the same way of storing data.
But, arrays can hold only a single data type elements whereas lists can hold any data type elements.
import array as arr
My_Array=arr.array('i',[1,2,3,4])
My_list=[1,'abc',1.20]
print(My_Array)
print(My_list)
array(‘i’, [1, 2, 3, 4]) [1, ‘abc’, 1.2]
What are functions in Python?
A function is a block of code which is executed only when it is called. To define a Python function, the def keyword is used.
def Newfunc():
print("Hi, Welcome to Edureka")
Newfunc(); #calling the function
Output: Hi, Welcome to Edureka
What is init?
init is a method or constructor in Python.
This method is automatically called to allocate memory when a new object/ instance of a class is created.
All classes have the init method.
class Employee:
def __init__(self, name, age,salary):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.salary = 20000
E1 = Employee("XYZ", 23, 20000)
# E1 is the instance of class Employee.
#__init__ allocates memory for E1.
print(E1.name)
print(E1.age)
print(E1.salary)
Output: XYZ 23 20000
What is a lambda function?
An anonymous function is known as a lambda function. This function can have any number of parameters but, can have just one statement.
addone = lambda x : x+1
print(addone(2))
3
What does [::-1} do?
[::-1] is used to reverse the order of an array or a sequence.
import array as arr
My_Array=arr.array('i',[1,2,3,4,5])
My_Array[::-1]
Output: array(‘i’, [5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
[::-1] reprints a reversed copy of ordered data structures such as an array or a list. the original array or list remains unchanged.
How can you randomize the items of a list in place in Python?
from random import shuffle
x = ['Keep', 'The', 'Blue', 'Flag', 'Flying', 'High']
shuffle(x)
print(x)
What are python iterators?
Ans: Iterators are objects which can be traversed though or iterated upon.
How can you generate random numbers in Python?
Random module is the standard module that is used to generate a random number. The method is defined as:
import random
random.random
How will you capitalize the first letter of string?
In Python, the capitalize() method capitalizes the first letter of a string. If the string already consists of a capital letter at the beginning, then, it returns the original string.
How will you convert a string to all lowercase?
To convert a string to lowercase, lower() function can be used.
stg='ABCD'
print(stg.lower())
Output: abcd
What is the purpose of is, not and in operators?
Operators are special functions. They take one or more values and produce a corresponding result. is: returns true when 2 operands are true (Example: “a” is ‘a’) not: returns the inverse of the boolean value in: checks if some element is present in some sequence
What is a dictionary in Python?
The built-in datatypes in Python is called dictionary. It defines one-to-one relationship between keys and values. Dictionaries contain pair of keys and their corresponding values. Dictionaries are indexed by keys.
Let’s take an example:
The following example contains some keys. Country, Capital & PM. Their corresponding values are India, Delhi and Modi respectively.
dict={'Country':'Italy','Capital':'Rome','Language':'Italian'}
print dict[Country]
Italy
How can the ternary operators be used in python?
The Ternary operator is the operator that is used to show the conditional statements. This consists of the true or false values with a statement that has to be evaluated for it. Syntax: The Ternary operator will be given as: [on_true] if [expression] else [on_false]x, y = 25, 50big = x if x < y else y
The expression gets evaluated like if x<y else y, in this case if x<y is true then the value is returned as big=x and if it is incorrect then big=y will be sent as a result.
What does this mean: *args, ** kwargs? And why would we use it?
We use *args when we aren’t sure how many arguments are going to be passed to a function, or if we want to pass a stored list or tuple of arguments to a function. ** kwargs is used when we don’t know how many keyword arguments will be passed to a function, or it can be used to pass the values of a dictionary as keyword arguments. The identifiers args and kwargs are a convention, you could also use *bob and **billy but that would not be wise.
What does len() do?
It is used to determine the length of a string, a list, an array, etc.
stg='ABCD'
len(stg)
Explain split(), sub(), subn() methods of “re” module in Python.
To modify the strings, Python’s “re” module is providing 3 methods. They are:
split() – uses a regex pattern to “split” a given string into a list. sub() – finds all substrings where the regex pattern matches and then replace them with a different string subn() – it is similar to sub() and also returns the new string along with the no. of replacements.
What are negative indexes and why are they used?
The sequences in Python are indexed and it consists of the positive as well as negative numbers.
The numbers that are positive uses ‘0’ that is uses as first index and ‘1’ as the second index and the process goes on like that.
The index for the negative number starts from ‘-1’ that represents the last index in the sequence and ‘-2’ as the penultimate index and the sequence carries forward like the positive number.
The negative index is used to remove any new-line spaces from the string and allow the string to except the last character that is given as S[:-1]. The negative index is also used to show the index to represent the string in correct order.
How to add values to a python array?
Elements can be added to an array using the append(), extend() and the insert (i,x) functions.
a=arr.array('d', [1.1 , 2.1 ,3.1] )
a.append(3.4)
print(a)
a.extend([4.5,6.3,6.8])
print(a)
a.insert(2,3.8)
print(a)
Output:
array(‘d’, [1.1, 2.1, 3.1, 3.4])
array(‘d’, [1.1, 2.1, 3.1, 3.4, 4.5, 6.3, 6.8])
array(‘d’, [1.1, 2.1, 3.8, 3.1, 3.4, 4.5, 6.3, 6.8])
How to remove values to a python array?
Array elements can be removed using pop() or remove() method. The difference between these two functions is that the former returns the deleted value whereas the latter does not.
a=arr.array('d', [1.1, 2.2, 3.8, 3.1, 3.7, 1.2, 4.6])
print(a.pop())
print(a.pop(3))
a.remove(1.1)
print(a)
What is split used for?
a="edureka python"
print(a.split())
Output: [‘edureka’, ‘python’]
How are classes created in Python?
Class in Python is created using the class keyword.
class Employee:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
E1=Employee("abc")
print(E1.name)
Output: abc
What is monkey patching in Python?
In Python, the term monkey patch only refers to dynamic modifications of a class or module at run-time.
Consider the below example:
# m.py
class MyClass:
def f(self):
print "f()"
We can then run the monkey-patch testing like this:
import m
def monkey_f(self):
print "monkey_f()"
m.MyClass.f = monkey_f
obj = m.MyClass()
obj.f()
The output will be as below:
monkey_f()
Additional questions
What is Agile ?

Agile is a time boxed, iterative approach to software delivery that builds software incrementally from the start of the project, instead of trying to deliver it all at once near the end.
What is Scrum ?
Scrum is a process framework used to manage product development and other knowledge work.
Scrum is empirical in that it provides a means for teams to establish a hypothesis of how they think something works, try it out, reflect on the experience, and make the appropriate adjustments. That is, when the framework is used properly.
Scrum is structured in a way that allows teams to incorporate practices from other frameworks where they make sense for the team’s context.
What is Ansible?
Ansible is an open-source software provisioning, configuration management, and application-deployment tool enabling infrastructure as code.
Ansible can easily run and configure Unix-like systems as well as Windows systems to provide infrastructure as code. Playbooks are the files where Ansible code is written. Playbooks are written in YAML format
Congratulations you have some of the concepts that any Data Engineer working in Spark should know . For sure there are a lot of more concepts that are missing here but I wanted only to summarize some of basic elements that are needed to begin to work in this area.

Leave a comment