Multiclass Classification of Hotels

Multiclass Classification
by Ruslan Magana Vsevolodovna
Genova November 2020

In this project we are going to classify the accommodations given by some features collected in one dataset. The target is the classification of the following types of accommodations:
- Hotel 1-3 stars
- Hotel 4+ stars
- Bed & Breakfast
- Campsites
- Houses / apartments
The dataset of the accommodations can downloaded from Github
1. Libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import itertools
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, KFold, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report, accuracy_score
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.utils import to_categorical
from keras.wrappers.scikit_learn import KerasClassifier
2. Data Wrangling
df=pd.read_csv ('classification_dataset.csv',sep = '\t', )
Replace NaN Values with Zeros in Pandas DataFrame For an entire DataFrame using Pandas:
df=df.fillna(0)
df.head()
| ID | PROVINCIA | COMUNE | LOCALITA | CAMERE | SUITE | LETTI | BAGNI | PRIMA_COLAZIONE | IN_ABITATO | ... | ZONA_PERIFERICA | ZONA_STAZIONE_FS | ATTREZZATURE_VARIE | CARTE_ACCETTATE | LINGUE_PARLATE | SPORT | CONGRESSI | LATITUDINE | LONGITUDINE | OUTPUT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | BS | PERTICA BASSA | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.373501 | 45.751381 | B&B |
| 1 | 1 | BS | DESENZANO DEL GARDA | 0 | 4 | 0 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.538947 | 45.469485 | B&B |
| 2 | 2 | BG | BERGAMO | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | Accettazione animali domestici | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9.665355 | 45.704158 | Case_Appartamenti |
| 3 | 3 | MN | MANTOVA | BOCCABUSA | 93 | 2 | 194 | 96 | 0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | Ascensore,Ristorante,Bar,Accettazione animali ... | American express,Visa,Master Card,Diners,Maest... | Inglese,Francese,Spagnolo,Tedesco,Rumeno,Serbo... | 0 | Numero sale congressi 3,Congressi capacita' Mi... | 10.828175 | 45.165506 | 4_a_5_Stelle |
| 4 | 4 | MI | MILANO | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9.151637 | 45.457177 | Case_Appartamenti |
5 rows × 25 columns
There are some features that do not gives important information: Such as: ID, LOCALITA, LATITUDINE LONGITUDINE
del df['ID']
del df['LOCALITA']
del df['LATITUDINE']
del df['LONGITUDINE']
del df['PROVINCIA']
del df['COMUNE']
dfa=df
One-hot Encoding is a type of vector representation in which all of the elements in a vector are 0, except for one, which has 1 as its value, where 1 represents a boolean specifying a category of the element.
new_df = pd.concat([dfa.drop('ATTREZZATURE_VARIE', 1), dfa['ATTREZZATURE_VARIE'].str.get_dummies(sep=",")], 1)
new_df2 = pd.concat([new_df.drop('CARTE_ACCETTATE', 1), new_df['CARTE_ACCETTATE'].str.get_dummies(sep=",")], 1)
new_df3 = pd.concat([new_df2.drop('LINGUE_PARLATE', 1), new_df2['LINGUE_PARLATE'].str.get_dummies(sep=",")], 1)
new_df4 = pd.concat([new_df3.drop('SPORT', 1), new_df3['SPORT'].str.get_dummies(sep=",")], 1)
new_df5 = pd.concat([new_df4.drop('CONGRESSI', 1), new_df4['CONGRESSI'].str.get_dummies(sep=",")], 1)
new_df5.describe()
| CAMERE | SUITE | LETTI | BAGNI | PRIMA_COLAZIONE | IN_ABITATO | SUL_LAGO | VICINO_ELIPORTO | VICINO_AEREOPORTO | ZONA_CENTRALE | ... | Numero sale congressi 17 | Numero sale congressi 2 | Numero sale congressi 21 | Numero sale congressi 3 | Numero sale congressi 4 | Numero sale congressi 5 | Numero sale congressi 6 | Numero sale congressi 7 | Numero sale congressi 8 | Numero sale congressi 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | ... | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.00000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 | 6775.000000 |
| mean | 16.261550 | 0.455646 | 35.002509 | 13.620517 | 0.101402 | 0.083542 | 0.052546 | 0.000590 | 0.027897 | 0.099041 | ... | 0.000295 | 0.008413 | 0.000148 | 0.004428 | 0.00428 | 0.001624 | 0.001328 | 0.001181 | 0.000886 | 0.000738 |
| std | 35.859435 | 3.592147 | 93.538492 | 29.174499 | 0.301883 | 0.276721 | 0.223142 | 0.024293 | 0.164689 | 0.298739 | ... | 0.017180 | 0.091344 | 0.012149 | 0.066401 | 0.06529 | 0.040264 | 0.036426 | 0.034345 | 0.029748 | 0.027158 |
| min | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | ... | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.00000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 25% | 2.000000 | 0.000000 | 4.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | ... | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.00000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 50% | 4.000000 | 0.000000 | 8.000000 | 3.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | ... | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.00000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 75% | 14.000000 | 0.000000 | 25.000000 | 12.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | ... | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.00000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| max | 528.000000 | 110.000000 | 1816.000000 | 448.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | ... | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.00000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 |
8 rows × 308 columns
Encode The Output Variable The output variable contains different string values.
When modeling multi-class classification problems using neural networks, it is good practice to reshape the output attribute from a vector that contains values for each class value to be a matrix with a boolean for each class value and whether or not a given instance has that class value or not.
new_df6 = pd.concat([new_df5.drop('OUTPUT', 1), new_df5['OUTPUT'].str.get_dummies(sep=",")], 1)
new_df6.dtypes
CAMERE int64
SUITE int64
LETTI int64
BAGNI int64
PRIMA_COLAZIONE int64
...
1_a_3_Stelle int64
4_a_5_Stelle int64
B&B int64
Campeggio int64
Case_Appartamenti int64
Length: 313, dtype: object
We have now all our fetures numeric we can use it.
We have several fetures. we can REDUCE the dimensions by using Principal Component Analysis ( PCA )but for lack of time, we just show the standard procedure to classify with the current status of the dataset.
3. MODEL CREATION
dataset=new_df6.to_numpy()
X = dataset[:,0:308].astype(float)
len(X)
6775
Y = dataset[:,308:]
len(Y)
6775
The Keras library provides wrapper classes to allow you to use neural network models developed with Keras in scikit-learn.
There is a KerasClassifier class in Keras that can be used as an Estimator in scikit-learn, the base type of model in the library. The KerasClassifier takes the name of a function as an argument. This function must return the constructed neural network model, ready for training.
Below is a function that will create a baseline neural network for the Accommodation classification problem. It creates a simple fully connected network with one hidden layer that contains 616 neurons.
The hidden layer uses a rectifier activation function which is a good practice. Because we used a one-hot encoding for our dataset, the output layer must create 5 output values, one for each class. The output value with the largest value will be taken as the class predicted by the model.
The network topology of this simple one-layer neural network can be summarized as:
308 inputs -> [616 hidden nodes] -> 5 outputs
Note that we use a “softmax” activation function in the output layer. This is to ensure the output values are in the range of 0 and 1 and may be used as predicted probabilities.
Finally, the network uses the efficient Adam gradient descent optimization algorithm with a logarithmic loss function, which is called “categorical_crossentropy” in Keras.
seed = 7
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, train_size=0.8, random_state=seed)
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(x_train, y_train, train_size=0.8, random_state=seed)
The hyperparameteres were computed in the optional section by using GridCSV
Best: 0.880295 using {‘batch_size’: 80, ‘epochs’: 200}
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(616,activation='relu',input_shape = (308,)))
model.add(Dense(5,activation='softmax'))
model.compile(optimizer = 'adam',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
history = model.fit(x_train,
y_train,
epochs = 200,
batch_size = 80,
verbose=0,
validation_data=(x_val,y_val))
4. RESULTS
We define some programs to visualize the results Plot History : plot loss and accuracy from the history Full Report : print a full report and plot a confusion matrix
def plot_history(history):
loss_list = [s for s in history.history.keys() if 'loss' in s and 'val' not in s]
val_loss_list = [s for s in history.history.keys() if 'loss' in s and 'val' in s]
acc_list = [s for s in history.history.keys() if 'acc' in s and 'val' not in s]
val_acc_list = [s for s in history.history.keys() if 'acc' in s and 'val' in s]
if len(loss_list) == 0:
print('Loss is missing in history')
return
## As loss always exists
epochs = range(1,len(history.history[loss_list[0]]) + 1)
## Loss
plt.figure(1)
for l in loss_list:
plt.plot(epochs, history.history[l], 'b', label='Training loss (' + str(str(format(history.history[l][-1],'.5f'))+')'))
for l in val_loss_list:
plt.plot(epochs, history.history[l], 'g', label='Validation loss (' + str(str(format(history.history[l][-1],'.5f'))+')'))
plt.title('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
## Accuracy
plt.figure(2)
for l in acc_list:
plt.plot(epochs, history.history[l], 'b', label='Training accuracy (' + str(format(history.history[l][-1],'.5f'))+')')
for l in val_acc_list:
plt.plot(epochs, history.history[l], 'g', label='Validation accuracy (' + str(format(history.history[l][-1],'.5f'))+')')
plt.title('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,
normalize=False,
cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
"""
This function prints and plots the confusion matrix.
Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`.
"""
if normalize:
cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
title='Normalized confusion matrix'
else:
title='Confusion matrix'
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
fmt = '.2f' if normalize else 'd'
thresh = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt),
horizontalalignment="center",
color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
plt.show()
## multiclass or binary report
## If binary (sigmoid output), set binary parameter to True
def full_multiclass_report(model,
x,
y_true,
classes,
batch_size=32,
binary=False):
# 1. Transform one-hot encoded y_true into their class number
if not binary:
y_true = np.argmax(y_true,axis=1)
# 2. Predict classes and stores in y_pred
y_pred = model.predict_classes(x, batch_size=batch_size)
# 3. Print accuracy score
print("Accuracy : "+ str(accuracy_score(y_true,y_pred)))
print("")
# 4. Print classification report
print("Classification Report")
print(classification_report(y_true,y_pred,digits=5))
# 5. Plot confusion matrix
cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_true,y_pred)
print(cnf_matrix)
plot_confusion_matrix(cnf_matrix,classes=classes)
Results
plot_history(history)
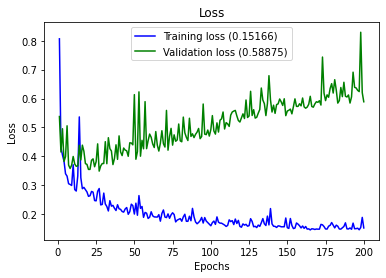
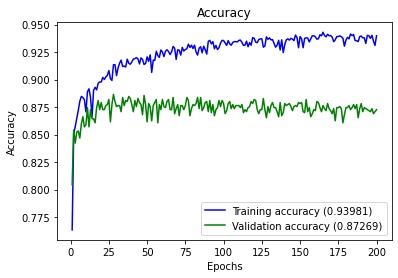
labels=list(new_df6.columns)[308:]
labels
['1_a_3_Stelle', '4_a_5_Stelle', 'B&B', 'Campeggio', 'Case_Appartamenti']
full_multiclass_report(model,
x_val,
y_val,
labels
)
WARNING:tensorflow:From <ipython-input-30-3b4d949a528c>:47: Sequential.predict_classes (from tensorflow.python.keras.engine.sequential) is deprecated and will be removed after 2021-01-01.
Instructions for updating:
Please use instead:* `np.argmax(model.predict(x), axis=-1)`, if your model does multi-class classification (e.g. if it uses a `softmax` last-layer activation).* `(model.predict(x) > 0.5).astype("int32")`, if your model does binary classification (e.g. if it uses a `sigmoid` last-layer activation).
Accuracy : 0.8726937269372693
Classification Report
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.86364 0.86008 0.86186 243
1 0.61111 0.59459 0.60274 74
2 0.93651 0.81944 0.87407 288
3 1.00000 0.82353 0.90323 17
4 0.87897 0.95887 0.91718 462
accuracy 0.87269 1084
macro avg 0.85804 0.81131 0.83182 1084
weighted avg 0.87443 0.87269 0.87164 1084
[[209 28 0 0 6]
[ 28 44 0 0 2]
[ 0 0 236 0 52]
[ 1 0 1 14 1]
[ 4 0 15 0 443]]
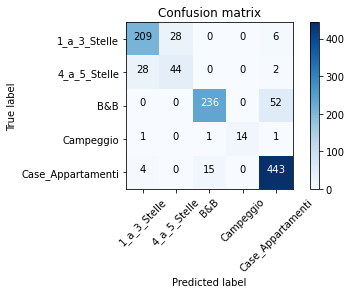
Additional comments
The results can be improved by using PCA and a Grid Search. GridSearchCV resolve the issue relative to the multiclass models when using custom scoring, find the best hyperparameters.
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.utils import np_utils
from keras.wrappers.scikit_learn import KerasClassifier
import numpy
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
def create_model():
# create model
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(2*308, input_dim=308, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(5, activation='softmax'))
# Compile model
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
# fix random seed for reproducibility
seed = 7
numpy.random.seed(seed)
# create model
model = KerasClassifier(build_fn=create_model, verbose=0)
# define the grid search parameters
batch_size = [5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100]
epochs = [10, 50, 100, 200]
param_grid = dict(batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epochs)
grid = GridSearchCV(estimator=model, param_grid=param_grid, n_jobs=1)
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
X, Y = shuffle(X, Y)
grid_result = grid.fit(X, Y)
# summarize results
print("Best: %f using %s" % (grid_result.best_score_, grid_result.best_params_))
means = grid_result.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
stds = grid_result.cv_results_['std_test_score']
params = grid_result.cv_results_['params']
for mean, stdev, param in zip(means, stds, params):
print("%f (%f) with: %r" % (mean, stdev, param))
Best: 0.880295 using {‘batch_size’: 80, ‘epochs’: 200}
which are the hyperparameters used before.
Congratulations! we classified with Neural Network the different types of accommodations.

Leave a comment